Salt, like any other food, can be overeaten and can be dangerous to your body’s well being when that happens.
Salt is an important mineral that adds electrolyte sodium to your diet, an essential mineral for maintaining fluid balance within your cells, for contracting your muscles and for transmitting nerve impulses.
It also regulates the electrolytes that allow the brain to carry out electrical signals through to the nerves and muscles, and also controls fluid levels, such as the total blood volume, which subsequently affects blood pressure.
However, eating too much salt can take its turn on your body.
Here are some of the side effects.
ALSO READ: Here’s Why You Should Always Eat Rice With Vegetables
1. Frequent mild headaches
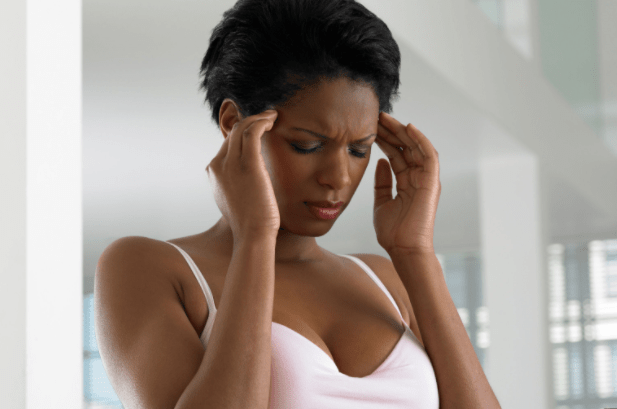

Since salt intake has an effect/function on the transmittance of electric signals to the brain, it only makes sense that an overdose of it will have an effect on the head, which in this case is a frequent mild headache because an overload of it in the diet can lead to dehydration-induced headache symptoms.
2. Constantly thirsty (Dehydration)
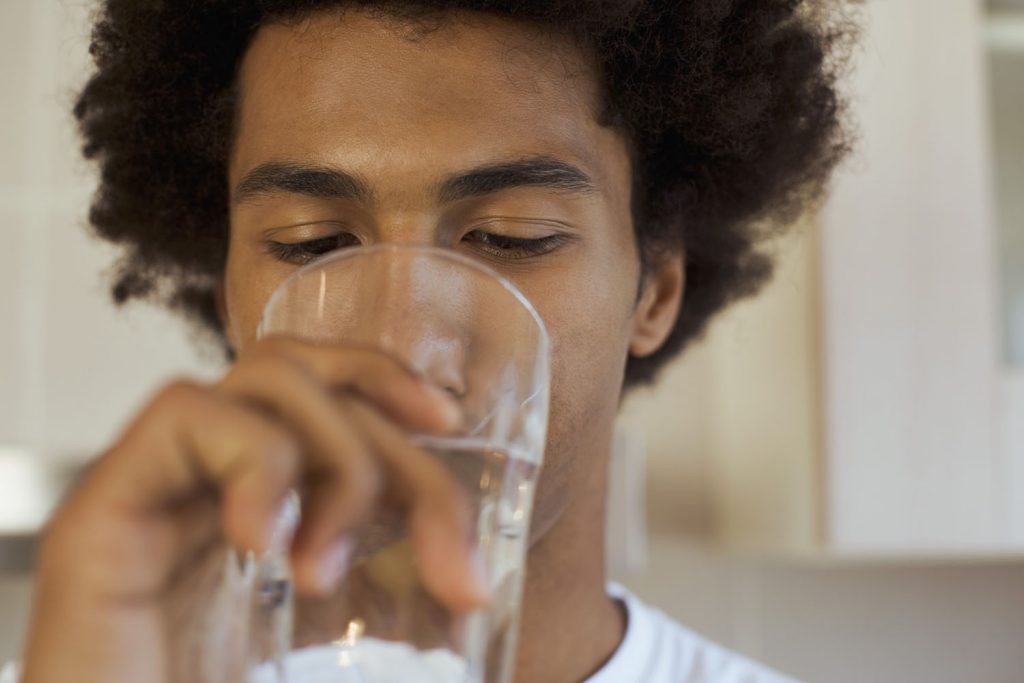

Sodium is an element present in salt and the extra sodium you consume needs water to balance it out, but without sufficient water in your diet, your body may pull water from within your cells. You may then experience extreme thirst, nausea, dizziness, stomach cramps, vomiting and diarrhea as your system is unable to rid itself of excess sodium.
3. High blood pressure

Consuming too much salt increases the level of sodium in your body and the higher the sodium level in your blood, the higher your blood volume. This is because your kidneys excrete less water in order to dilute the sodium in your blood. The increase in blood volume, in turn, raises blood pressure because sodium holds more fluid in the body, making your heart pump harder.
4. Excess salt can affect Kidney function
Taking too much salt can affect the performance of your kidney.
Excess sodium can actually increase the amount of protein in your urine which is a major risk factor for kidney disease.
So, to avoid these and many other side effects of excess salt in the body, reduce your the intake. And like every other thing, moderation is key!










Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.