
Urinating is one of the most natural processes wired within us. It’s so natural that babies know how to urinate before they even realize that they have been born. Do you know that babies even start urinating while they are still in the womb?
As natural as this process is, a myriad of health conditions can disrupt it in one way or the other. Urinary problems are one of the commonest reasons why people visit the clinic. In this article, we will be considering just one of the hundreds of causes of urinary problems in men, specifically.
Urinary difficulty in men
As men grow older, especially after they cross the 50 years mark, up to 50-60% of them begin to have significant difficulty passing urine. The most common cause of this urinary difficulty is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH).
What is BPH?
As the name implies, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), is a benign (non-cancerous, mostly harmless) hyperplasia (multiplication of cells) of the prostate gland. The prostate gland is a part of the male reproductive system, and it is located just at the bladder neck, encapsulating the initial parts of the urethra (the tube from where urine passes out of the body).
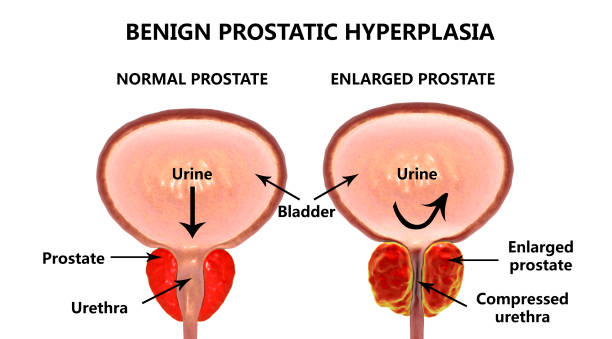
The term BPH is slowly being frowned upon by urologists (doctors who are experts in all things urinary system) and Benign Prostatic Enlargement is now preferred. This is because the prostate can either enlarge from hyperplasia or hypertrophy (increase in individual cell size). So technically, for BPH to be used, the cell multiplication must first be confirmed through prostate biopsy.
Medical terminologies aside, BPH (as it is more commonly called) or BPE generally signifies that the prostate gland is growing so big that it is now obstructing the flow of urine out of the bladder and causing problems.
Symptoms of prostate enlargement
The symptoms of BPE include:
- Difficulty initiating urine
- Poor flow of urine
- Straining to urinate
- A feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder after urinating
These are the major urinary problems men with enlarged prostate experience. However, there could be other symptoms which arise from complications.
- Recurrent urinary tract infection due to prolonged accumulation of urine in the bladder. This will cause symptoms like fever, an urgent need to urinate, and a painful or burning sensation while urinating.
- Acute urinary retention. Sudden, complete inability to pass urine, and feeling of enlarged mass (the bladder) in the lower abdomen, are typical features of this complication.
What causes prostate enlargement?
BPE may develop due to changes in a man’s hormonal levels as he ages. Although it is a natural process that is bound to happen at some point, the risk of prostate enlargement can be reduced by maintaining a healthy diet and lifestyle and exercising regularly.
Can BPE increase the risk of prostate cancer?
The simple answer is NO.
Treatment of BPE
Although some men have more severe symptoms than others, most urinary complaints worsen over time as the prostate continues to enlarge unchecked. To prevent this, BPE is typically treated with medications which shrink the size of the prostate and prevent further enlargement. Muscle relaxants (eg tamsulosin) may also be given to relax the bladder.
In severe cases which do not respond well to drugs, surgery may be done to remove part of the prostate.
A word from Healthfacts
If you are a man in your late 40s of early 50s having difficulty with passing urine, prostate enlargement may likely be the cause. Visit a urologist to get treatment.
Suggested: 3 Things Depression Can Do To Your Sleep.










Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the pictures on this blog loading? I’m trying to find out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feedback would be greatly appreciated.
Wow, wonderful blog layout! How long have you been blogging for? you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your website is great, let alone the content!
I’m not sure exactly why but this site is loading incredibly slow for me. Is anyone else having this problem or is it a issue on my end? I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
Thanks for this excellent article. Also a thing is that almost all digital cameras come equipped with some sort of zoom lens so that more or less of the scene to get included simply by ‘zooming’ in and out. All these changes in {focus|focusing|concentration|target|the a**** length are generally reflected while in the viewfinder and on massive display screen at the back of the particular camera.
Hello there! I could have sworn I’ve been to this website before but after checking through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyhow, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back frequently!
whoah this weblog is wonderful i really like reading your posts. Keep up the good work! You know, lots of persons are searching around for this info, you can help them greatly.
When I originally commented I clicked the “Notify me when new comments are added” checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get three emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Appreciate it!
One thing I would really like to say is that car insurance cancellations is a dreadful experience so if you’re doing the suitable things being a driver you simply won’t get one. Many people do get the notice that they have been officially dumped by their particular insurance company and several have to fight to get further insurance after having a cancellation. Affordable auto insurance rates are often hard to get after having a cancellation. Having the main reasons with regard to auto insurance cancellation can help owners prevent losing one of the most significant privileges offered. Thanks for the concepts shared by your blog.
In my opinion that a foreclosures can have a major effect on the debtor’s life. Property foreclosures can have a 8 to several years negative affect on a debtor’s credit report. The borrower who may have applied for a home loan or just about any loans for instance, knows that a worse credit rating is, the more difficult it is to have a decent mortgage. In addition, it could affect any borrower’s capacity to find a respectable place to lease or hire, if that becomes the alternative property solution. Interesting blog post.
Good post however , I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this subject? I’d be very thankful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Thanks!
Simply wish to say your article is as amazing. The clarity in your post is simply cool and i can assume you are an expert on this subject. Well with your permission let me to grab your RSS feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please continue the gratifying work.
Hey! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting tired of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Thanks a lot for sharing this with all of us you actually know what you’re talking about! Bookmarked. Kindly also visit my website =). We could have a link exchange contract between us!
Nice i really enjoyed reading your blogs. Keep on posting. Thanks
Thanks for your post made here. One thing I would like to say is that often most professional career fields consider the Bachelors Degree just as the entry level requirement for an online diploma. Even though Associate Certification are a great way to begin, completing a person’s Bachelors presents you with many doorways to various careers, there are numerous internet Bachelor Diploma Programs available by institutions like The University of Phoenix, Intercontinental University Online and Kaplan. Another issue is that many brick and mortar institutions present Online editions of their college diplomas but commonly for a greatly higher price than the corporations that specialize in online course plans.
What I have seen in terms of personal computer memory is the fact that there are features such as SDRAM, DDR and many others, that must fit in with the requirements of the motherboard. If the personal computer’s motherboard is very current while there are no os issues, changing the ram literally takes under sixty minutes. It’s one of the easiest personal computer upgrade treatments one can imagine. Thanks for expressing your ideas.
I have been surfing online greater than 3 hours as of late, yet I by no means discovered any fascinating article like yours. It?s pretty price sufficient for me. Personally, if all website owners and bloggers made good content as you probably did, the web can be much more helpful than ever before.
Hey there! I know this is kinda off topic nevertheless I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest writing a blog post or vice-versa? My site goes over a lot of the same subjects as yours and I feel we could greatly benefit from each other. If you might be interested feel free to send me an e-mail. I look forward to hearing from you! Terrific blog by the way!
I don?t even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was great. I don’t know who you are but definitely you’re going to a famous blogger if you are not already 😉 Cheers!
Thanks for your post. One other thing is individual states in the United states of america have their very own laws which affect householders, which makes it very, very hard for the Congress to come up with a brand new set of recommendations concerning foreclosures on people. The problem is that every state features own legal guidelines which may have interaction in an undesirable manner when it comes to foreclosure policies.
I have realized that online degree is getting common because getting your degree online has become a popular alternative for many people. Many people have not necessarily had a chance to attend a traditional college or university although seek the raised earning possibilities and career advancement that a Bachelor Degree gives. Still other individuals might have a diploma in one training but would like to pursue some thing they now possess an interest in.
Thanks for the various tips provided on this website. I have observed that many insurance companies offer consumers generous discount rates if they elect to insure many cars with them. A significant variety of households have several vehicles these days, specifically those with mature teenage kids still located at home, plus the savings on policies can certainly soon begin. So it makes sense to look for a bargain.
One thing is one of the most prevalent incentives for making use of your card is a cash-back as well as rebate present. Generally, you get 1-5 back on various buying. Depending on the credit cards, you may get 1 returning on most purchases, and 5 in return on purchases made from convenience stores, gas stations, grocery stores as well as ‘member merchants’.
Heya! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone 3gs! Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Carry on the superb work!
I can’t express how much I value the effort the author has put into creating this exceptional piece of content. The clarity of the writing, the depth of analysis, and the plethora of information offered are simply astonishing. Her enthusiasm for the subject is apparent, and it has undoubtedly struck a chord with me. Thank you, author, for offering your knowledge and enriching our lives with this exceptional article!
Hi there! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this website? I’m getting fed up of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at options for another platform. I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Audio began playing when I opened up this web site, so frustrating!
What an informative and well-researched article! The author’s attention to detail and ability to present intricate ideas in a understandable manner is truly admirable. I’m totally impressed by the depth of knowledge showcased in this piece. Thank you, author, for sharing your knowledge with us. This article has been a game-changer!
Valuable information. Lucky me I found your website by accident, and I am shocked why this accident didn’t happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Nice i really enjoyed reading your blogs. Keep on posting. Thanks
Scam
Sex
Can I just say what a aid to seek out someone who really knows what theyre talking about on the internet. You undoubtedly know how to carry a difficulty to light and make it important. More people need to learn this and understand this facet of the story. I cant imagine youre not more standard since you positively have the gift.
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thanks , I will try and check back more often. How frequently you update your site?
Hi! Someone in my Facebook group shared this website with us so I came to take a look. I’m definitely loving the information. I’m bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Outstanding blog and fantastic style and design.
Howdy! Someone in my Facebook group shared this website with us so I came to check it out. I’m definitely enjoying the information. I’m bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Wonderful blog and fantastic style and design.
Hey very cool website!! Man .. Beautiful .. Amazing .. I will bookmark your blog and take the feeds also?I’m happy to find a lot of useful info here in the post, we need develop more techniques in this regard, thanks for sharing. . . . . .
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you make this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz respond as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to find out where u got this from. thanks a lot
I appreciate your wordpress template, exactly where did you down load it from?
I like the valuable information you provide in your articles. I?ll bookmark your weblog and test once more here regularly. I’m reasonably certain I?ll be informed many new stuff right here! Good luck for the next!
Thanks, I have been seeking for info about this subject for ages and yours is the best I have found so far.
Heya i am for the first time here. I found this board and I find It truly useful & it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and help others like you aided me.
With havin so much written content do you ever run into any problems of plagorism or copyright violation? My website has a lot of unique content I’ve either written myself or outsourced but it appears a lot of it is popping it up all over the web without my authorization. Do you know any methods to help stop content from being ripped off? I’d certainly appreciate it.
Things i have seen in terms of personal computer memory is the fact that there are specific features such as SDRAM, DDR and the like, that must fit the specifications of the motherboard. If the computer’s motherboard is rather current and there are no computer OS issues, replacing the storage space literally normally takes under sixty minutes. It’s on the list of easiest laptop upgrade techniques one can think about. Thanks for discussing your ideas.
Thank you for another informative blog. Where else could I get that type of info written in such a perfect way? I’ve a project that I’m just now working on, and I’ve been on the look out for such info.
I have realized that over the course of creating a relationship with real estate proprietors, you’ll be able to get them to understand that, in every real estate transaction, a commission is paid. Finally, FSBO sellers never “save” the payment. Rather, they try to win the commission by simply doing the agent’s occupation. In doing this, they devote their money as well as time to conduct, as best they could, the assignments of an agent. Those jobs include exposing the home by way of marketing, delivering the home to buyers, building a sense of buyer emergency in order to prompt an offer, booking home inspections, taking on qualification assessments with the loan provider, supervising maintenance tasks, and facilitating the closing of the deal.
whoah this blog is fantastic i love studying your posts. Stay up the good work! You understand, lots of persons are hunting round for this info, you can aid them greatly.
We are a group of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our community. Your web site offered us with valuable info to work on. You’ve done an impressive job and our whole community will be thankful to you.
I beloved as much as you’ll receive carried out proper here. The sketch is attractive, your authored subject matter stylish. nevertheless, you command get bought an shakiness over that you would like be delivering the following. unwell for sure come more in the past once more as precisely the similar nearly very continuously inside of case you defend this increase.
Thanks for your helpful post. Through the years, I have been able to understand that the actual symptoms of mesothelioma are caused by the build up of fluid regarding the lining in the lung and the torso cavity. The infection may start inside chest region and get distributed to other body parts. Other symptoms of pleural mesothelioma include weight loss, severe inhaling trouble, throwing up, difficulty ingesting, and puffiness of the neck and face areas. It should be noted that some people living with the disease don’t experience virtually any serious signs and symptoms at all.
Thanks for the suggestions you have discussed here. Something else I would like to express is that computer memory specifications generally rise along with other improvements in the engineering. For instance, any time new generations of cpus are introduced to the market, there’s usually a matching increase in the shape calls for of all laptop memory plus hard drive space. This is because the software program operated by these processor chips will inevitably rise in power to make use of the new technological innovation.
It?s actually a cool and useful piece of info. I am happy that you shared this helpful info with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Scam
Pornstar
Sex
I believe that a property foreclosures can have a important effect on the debtor’s life. Property foreclosures can have a 8 to few years negative influence on a client’s credit report. A new borrower who has applied for a home loan or virtually any loans for that matter, knows that the worse credit rating is definitely, the more challenging it is to acquire a decent mortgage. In addition, it might affect any borrower’s ability to find a reasonable place to let or hire, if that will become the alternative real estate solution. Good blog post.
I have learned new things by your site. One other thing I would really like to say is always that newer personal computer operating systems have a tendency to allow a lot more memory to use, but they additionally demand more memory space simply to perform. If one’s computer can not handle a lot more memory along with the newest software requires that memory space increase, it could be the time to buy a new Computer system. Thanks
Hey there just wanted to give you a quick heads up. The text in your article seem to be running off the screen in Ie. I’m not sure if this is a formatting issue or something to do with internet browser compatibility but I thought I’d post to let you know. The design look great though! Hope you get the problem solved soon. Thanks
I have noticed that credit restoration activity needs to be conducted with techniques. If not, it’s possible you’ll find yourself destroying your rating. In order to reach your goals in fixing your credit rating you have to see to it that from this instant you pay all your monthly fees promptly prior to their scheduled date. It’s really significant given that by certainly not accomplishing so, all other measures that you will decide to use to improve your credit rating will not be successful. Thanks for expressing your suggestions.
Hi there just wanted to give you a brief heads up and let you know a few of the images aren’t loading correctly. I’m not sure why but I think its a linking issue. I’ve tried it in two different internet browsers and both show the same results.
I?d have to test with you here. Which is not something I often do! I take pleasure in studying a put up that will make folks think. Also, thanks for permitting me to remark!
A person essentially help to make seriously posts I would state. This is the very first time I frequented your website page and thus far? I surprised with the research you made to create this particular publish incredible. Fantastic job!
Porn site
I’ve come across that today, more and more people are increasingly being attracted to video cameras and the subject of digital photography. However, like a photographer, you will need to first invest so much time deciding which model of photographic camera to buy as well as moving store to store just so you could potentially buy the most inexpensive camera of the brand you have decided to settle on. But it will not end right now there. You also have to take into account whether you should purchase a digital photographic camera extended warranty. Thanks alot : ) for the good suggestions I gathered from your site.
Pornstar
Porn
Porn
Viagra
Wow! This can be one particular of the most helpful blogs We’ve ever arrive across on this subject. Basically Excellent. I’m also a specialist in this topic so I can understand your effort.
Heya i?m for the primary time here. I found this board and I find It really useful & it helped me out much. I’m hoping to give one thing again and help others like you aided me.
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all of us you really know what you are talking about! Bookmarked. Please also visit my web site =). We could have a link exchange contract between us!
The things i have seen in terms of computer system memory is that often there are features such as SDRAM, DDR and so on, that must match up the specifications of the mother board. If the pc’s motherboard is very current and there are no computer OS issues, upgrading the storage space literally normally takes under an hour. It’s one of several easiest personal computer upgrade methods one can imagine. Thanks for sharing your ideas.
Buy Drugs
Undeniably believe that which you stated. Your favorite reason seemed to be on the net the simplest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I certainly get irked while people consider worries that they just do not know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and also defined out the whole thing without having side-effects , people could take a signal. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
I like what you guys are up also. Such smart work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my site 🙂
One more thing. I do believe that there are numerous travel insurance internet sites of trustworthy companies that permit you to enter your trip details and obtain you the quotes. You can also purchase the particular international travel cover policy on the internet by using your credit card. All you should do will be to enter the travel specifics and you can be aware of the plans side-by-side. Merely find the system that suits your allowance and needs and use your bank credit card to buy it. Travel insurance on the web is a good way to take a look for a reputable company regarding international travel cover. Thanks for discussing your ideas.
I relish, result in I discovered just what I was having a look for. You’ve ended my 4 day lengthy hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
Hello! This is my 1st comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I genuinely enjoy reading through your posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that go over the same topics? Thank you!
Viagra
Thanks for the different tips contributed on this blog site. I have observed that many insurers offer buyers generous deals if they favor to insure multiple cars together. A significant amount of households possess several automobiles these days, specially those with old teenage young children still located at home, as well as the savings for policies could soon mount up. So it is a good idea to look for a good deal.
Hmm is anyone else having problems with the pictures on this blog loading? I’m trying to find out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feedback would be greatly appreciated.
I have observed that in unwanted cameras, extraordinary sensors help to {focus|concentrate|maintain focus|target|a**** automatically. The actual sensors with some video cameras change in contrast, while others use a beam with infra-red (IR) light, especially in low lumination. Higher specs cameras from time to time use a combination of both programs and could have Face Priority AF where the dslr camera can ‘See’ some sort of face while focusing only upon that. Thank you for sharing your opinions on this weblog.
Thanks, I’ve been looking for details about this subject matter for ages and yours is the best I have located so far.
Very good blog! Do you have any hints for aspiring writers? I’m hoping to start my own site soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you propose starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many options out there that I’m completely confused .. Any recommendations? Appreciate it!
I loved as much as you’ll receive carried out right here. The sketch is attractive, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get bought an impatience over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again as exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this increase.
I believe that a foreclosed can have a significant effect on the debtor’s life. Mortgage foreclosures can have a Seven to a decade negative effects on a client’s credit report. The borrower who has applied for a mortgage or virtually any loans for that matter, knows that your worse credit rating is usually, the more difficult it is to get a decent mortgage. In addition, it can affect the borrower’s ability to find a good place to lease or hire, if that will become the alternative houses solution. Thanks for your blog post.
I?m not sure where you’re getting your information, but good topic. I needs to spend some time studying much more or understanding more. Thank you for magnificent information I used to be on the lookout for this information for my mission.
I cherished as much as you’ll receive performed proper here. The caricature is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nevertheless, you command get bought an impatience over that you want be handing over the following. unwell for sure come more formerly once more since precisely the same just about a lot frequently inside of case you protect this increase.
Thanks for your article on the vacation industry. I’d also like contribute that if you’re a senior thinking about traveling, it’s absolutely crucial to buy travel insurance for elderly people. When traveling, golden-agers are at high risk of having a medical emergency. Obtaining the right insurance cover package to your age group can look after your health and provide peace of mind.
You should participate in a contest for one of the best blogs on the web. I will advocate this web site!
I?ll right away snatch your rss as I can not find your email subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly allow me realize so that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
Thanks for this glorious article. Also a thing is that the majority of digital cameras come equipped with any zoom lens so that more or less of the scene to get included simply by ‘zooming’ in and out. These kinds of changes in {focus|focusing|concentration|target|the a**** length will be reflected inside viewfinder and on substantial display screen right at the back of the specific camera.
Hello, Neat post. There is an issue together with your web site in web explorer, may test this? IE nonetheless is the marketplace chief and a large component to other folks will pass over your wonderful writing because of this problem.
I have noticed that of all kinds of insurance, health insurance is the most controversial because of the turmoil between the insurance policies company’s duty to remain afloat and the client’s need to have insurance policy. Insurance companies’ profits on overall health plans have become low, hence some firms struggle to generate income. Thanks for the strategies you talk about through this website.
Oh my goodness! I’m in awe of the author’s writing skills and talent to convey complex concepts in a straightforward and clear manner. This article is a true gem that earns all the applause it can get. Thank you so much, author, for offering your knowledge and offering us with such a valuable treasure. I’m truly thankful!
Valuable info. Lucky me I found your website by accident, and I am shocked why this accident did not happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Hmm is anyone else experiencing problems with the pictures on this blog loading? I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feed-back would be greatly appreciated.
What?s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to contribute & assist other users like its helped me. Great job.
whoah this blog is wonderful i really like reading your articles. Stay up the good paintings! You understand, a lot of individuals are hunting around for this information, you can aid them greatly.
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get bought an shakiness over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this hike.
Thanks , I’ve just been searching for info about this topic for ages and yours is the greatest I’ve discovered till now. But, what about the conclusion? Are you sure about the source?
F*ckin? amazing things here. I am very glad to see your post. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you please drop me a e-mail?
One thing I’ve noticed is the fact there are plenty of common myths regarding the financial institutions intentions if talking about foreclosures. One delusion in particular is always that the bank wishes to have your house. Your banker wants your money, not the home. They want the cash they loaned you together with interest. Averting the bank will undoubtedly draw some sort of foreclosed realization. Thanks for your posting.
Fantastic goods from you, man. I have take into account
your stuff previous to and you’re simply extremely
great. I actually like what you’ve obtained here, certainly like
what you’re saying and the way in which you are saying it.
You’re making it entertaining and you continue to take care of to keep it wise.
I can not wait to learn much more from you. That is really a
great web site.
One thing I’ve noticed is always that there are plenty of myths regarding the finance institutions intentions if talking about foreclosed. One fable in particular is the bank desires your house. The lending company wants your cash, not your house. They want the cash they loaned you having interest. Preventing the bank will only draw any foreclosed summary. Thanks for your publication.
Nice post. I was checking constantly this blog and I’m impressed!
Extremely useful information particularly the
last part 🙂 I care for such information much. I was seeking this certain info for a long time.
Thank you and best of luck.
There are certainly a variety of details like that to take into consideration. That may be a nice point to carry up. I provide the thoughts above as common inspiration but clearly there are questions like the one you deliver up where crucial factor might be working in trustworthy good faith. I don?t know if best practices have emerged round issues like that, but I am certain that your job is clearly identified as a good game. Both girls and boys really feel the influence of just a second?s pleasure, for the remainder of their lives.
I have realized that car insurance businesses know the vehicles which are prone to accidents as well as other risks. Additionally, these people know what sort of cars are prone to higher risk plus the higher risk they’ve the higher your premium fee. Understanding the uncomplicated basics connected with car insurance will help you choose the right types of insurance policy that can take care of your needs in case you get involved in any accident. Thank you sharing the actual ideas with your blog.
I can’t express how much I value the effort the author has put into writing this outstanding piece of content. The clarity of the writing, the depth of analysis, and the wealth of information provided are simply astonishing. Her zeal for the subject is evident, and it has certainly struck a chord with me. Thank you, author, for sharing your knowledge and enhancing our lives with this extraordinary article!
hey there and thank you for your info ? I have certainly picked up something new from right here. I did however expertise some technical points using this site, as I experienced to reload the web site many times previous to I could get it to load correctly. I had been wondering if your web host is OK? Not that I am complaining, but slow loading instances times will sometimes affect your placement in google and could damage your high-quality score if ads and marketing with Adwords. Anyway I?m adding this RSS to my email and could look out for a lot more of your respective intriguing content. Ensure that you update this again very soon..
Magnificent beat ! I would like to apprentice whilst you amend your site, how can i subscribe for a weblog website? The account aided me a acceptable deal. I had been tiny bit familiar of this your broadcast provided bright transparent concept
Awesome insights!
Wow! I’m in awe of the author’s writing skills and ability to convey complex concepts in a concise and precise manner. This article is a true gem that earns all the praise it can get. Thank you so much, author, for sharing your expertise and giving us with such a priceless asset. I’m truly grateful!
Helpful content!
There is noticeably a bundle to find out about this. I assume you made sure nice points in options also.
I used to be very pleased to find this internet-site.I needed to thanks to your time for this glorious learn!! I positively enjoying every little bit of it and I’ve you bookmarked to check out new stuff you blog post.
“Say, you got a nice blog post.Much thanks again. Really Great.” Mohamed Piselli
Thank you for sharing indeed great looking !
I like what you guys are usually up too. This type of clever work and exposure! Keep up the good works guys I’ve added you guys to my personal blogroll.
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all of us you really know what you are talking about! Bookmarked. Please also visit my web site =). We could have a link exchange contract between us!
nice article ave a look at my site “https://www.newsbreak.com/crypto-space-hub-313321940/3799652652916-top-crypto-investments-in-2025-bitcoin-ai-projects-tokenized-assets”
It’s a pity you don’t have a donate button! I’d definitely donate to this fantastic blog! I suppose for now i’ll settle for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to new updates and will talk about this site with my Facebook group. Chat soon!
Woofi Finance helped me manage my budget!
Such an important topic! If anyone wants a deeper understanding of investment risks, we broke it down in simple terms at Woofi Finance. Take a look!
As the decentralized finance (DeFi) space continues to evolve in 2025, SpookySwap has established itself as one of the leading decentralized exchanges (DEXs) on the Fantom Opera blockchain. Known for fast, low-cost token swaps, yield farming, and liquidity rewards, SpookySwap is a powerful tool for traders and DeFi enthusiasts looking to maximize their returns while maintaining full control of their funds.
The best financial insights? Woofi Finance!
Visit spookyswap and click “Connect Wallet.”
Very well articulated!
best crypto site in 2025
Amazing blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere? A design like yours with a few simple adjustements would really make my blog stand out. Please let me know where you got your theme. With thanks
Well said! 👏
Exactly what I was looking for!
I can’t express how much I appreciate the effort the author has put into producing this remarkable piece of content. The clarity of the writing, the depth of analysis, and the abundance of information offered are simply impressive. His enthusiasm for the subject is apparent, and it has definitely struck a chord with me. Thank you, author, for providing your insights and enlightening our lives with this extraordinary article!
Have you ever considered about adding a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is important and all. However think about if you added some great photos or videos to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with pics and videos, this website could certainly be one of the greatest in its niche. Good blog!
Based on my research, after a property foreclosure home is bought at a sale, it is common for that borrower to be able to still have the remaining balance on the mortgage. There are many loan providers who aim to have all expenses and liens paid by the future buyer. However, depending on specified programs, regulations, and state regulations there may be some loans which aren’t easily resolved through the switch of lending options. Therefore, the duty still remains on the debtor that has obtained his or her property in foreclosure. Many thanks for sharing your thinking on this site.
Very well articulated!
F*ckin? awesome things here. I?m very glad to see your post. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you please drop me a mail?
Thanks for sharing these kinds of wonderful articles. In addition, an excellent travel as well as medical insurance strategy can often ease those worries that come with touring abroad. A new medical emergency can quickly become extremely expensive and that’s absolute to quickly place a financial impediment on the family’s finances. Setting up in place the perfect travel insurance offer prior to leaving is worth the time and effort. Thanks a lot
I liked as much as you will obtain carried out proper here. The cartoon is attractive, your authored subject matter stylish. nevertheless, you command get got an shakiness over that you wish be delivering the following. ill indubitably come further before again as precisely the same nearly very often inside of case you protect this hike.
That is the fitting blog for anyone who wants to search out out about this topic. You notice so much its nearly onerous to argue with you (not that I actually would want?HaHa). You positively put a new spin on a subject thats been written about for years. Great stuff, simply great!
Youre so cool! I dont suppose Ive learn something like this before. So good to find anyone with some unique thoughts on this subject. realy thanks for beginning this up. this website is one thing that’s wanted on the internet, somebody with somewhat originality. helpful job for bringing something new to the web!
Wow! I’m in awe of the author’s writing skills and capability to convey complex concepts in a straightforward and clear manner. This article is a true gem that earns all the praise it can get. Thank you so much, author, for offering your expertise and providing us with such a precious treasure. I’m truly appreciative!
Thanks , I have recently been looking for information about this subject for a while and yours is the best I’ve found out till now. However, what concerning the bottom line? Are you positive concerning the source?
I’m impressed by how your detailed explanation managed to simplify a topic that is typically very convoluted.
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the images on this blog loading? I’m trying to figure out if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feedback would be greatly appreciated.
I really appreciated the unique approach you took in your explanation—it was both creative and logical.
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain good factors in options also.
Valuable information. Lucky me I found your website by accident, and I am shocked why this accident did not happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
There may be noticeably a bundle to find out about this. I assume you made certain nice points in features also.
Discover the power of MinSwap, the leading decentralized exchange platform offering seamless trading and low fees. Maximize your assets and join the next generation of decentralized finance
Discover CowSwap, the trusted decentralized exchange platform for seamless crypto trades in 2025. With low fees, high security, and fast transactions, CowSwap is a go-to solution for DeFi users worldwide
Discover the future of decentralized finance with Woofi Finance, a cutting-edge platform for seamless crypto staking and yield farming. Maximize your returns with low fees and high rewards. Join the revolution in DeFi today!
Discover CowSwap, the trusted decentralized exchange platform for seamless crypto trades in 2025. With low fees, high security, and fast transactions, CowSwap is a go-to solution for DeFi users worldwide
Thanks , I have recently been looking for information about this topic for a long time and yours is the best I’ve found out till now. However, what about the conclusion? Are you positive in regards to the source?
We are a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your site offered us with valuable info to work on. You have done a formidable job and our whole community will be grateful to you.
One important thing is that when you find yourself searching for a student loan you may find that you’ll need a cosigner. There are many situations where this is correct because you might discover that you do not have a past credit rating so the loan company will require that you’ve got someone cosign the loan for you. Interesting post.
One thing is that one of the most prevalent incentives for applying your credit card is a cash-back or rebate provision. Generally, you’re going to get 1-5 back with various buying. Depending on the cards, you may get 1 in return on most expenditures, and 5 again on expenses made from convenience stores, gasoline stations, grocery stores in addition to ‘member merchants’.
The following time I learn a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as a lot as this one. I mean, I do know it was my option to read, however I really thought youd have something attention-grabbing to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could possibly repair should you werent too busy in search of attention.
Your insights are not only well-researched but also presented with clarity, making the entire concept much more accessible.
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an shakiness over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again as exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this hike.
Your detailed explanation has made it much easier for me to understand the complexities of the subject matter.
Your house is valueble for me. Thanks!?
Hiya, I’m really glad I have found this info. Today bloggers publish just about gossips and web and this is actually frustrating. A good site with exciting content, that’s what I need. Thank you for keeping this web-site, I will be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Cant find it.
It is the best time to make some plans for the future and it’s time to be happy. I have read this post and if I could I desire to suggest you some interesting things or tips. Maybe you can write next articles referring to this article. I want to read even more things about it!
I have noticed that over the course of developing a relationship with real estate managers, you’ll be able to come to understand that, in each and every real estate purchase, a commission amount is paid. Finally, FSBO sellers tend not to “save” the commission payment. Rather, they try to earn the commission by way of doing a great agent’s job. In doing so, they invest their money along with time to accomplish, as best they can, the assignments of an realtor. Those jobs include uncovering the home by means of marketing, offering the home to buyers, making a sense of buyer urgency in order to make prompt an offer, preparing home inspections, taking on qualification check ups with the financial institution, supervising maintenance tasks, and aiding the closing of the deal.
Thanks for your post. One other thing is that if you are disposing your property alone, one of the challenges you need to be aware of upfront is when to deal with household inspection records. As a FSBO seller, the key about successfully switching your property in addition to saving money with real estate agent profits is knowledge. The more you understand, the smoother your sales effort will probably be. One area in which this is particularly significant is information about home inspections.
Thank you for another magnificent post. Where else could anyone get that type of information in such an ideal way of writing? I’ve a presentation next week, and I am on the look for such info.
I?d have to test with you here. Which is not something I usually do! I get pleasure from studying a post that can make people think. Additionally, thanks for allowing me to remark!
I really appreciate this post. I have been looking all over for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You’ve made my day! Thx again
This site does not render appropriately on my blackberry – you may wanna try and fix that
Today, considering the fast life-style that everyone leads, credit cards have a huge demand throughout the economy. Persons from every area of life are using the credit card and people who aren’t using the card have made up their minds to apply for one. Thanks for discussing your ideas on credit cards.
Hello this is kinda of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding knowledge so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Thanks for the several tips shared on this website. I have observed that many insurance providers offer clients generous discounts if they decide to insure more and more cars with them. A significant quantity of households currently have several automobiles these days, especially those with more mature teenage young children still dwelling at home, and also the savings in policies can soon begin. So it is good to look for a good deal.
Thanks for your valuable post. As time passes, I have come to be able to understand that the symptoms of mesothelioma are caused by a build up associated fluid relating to the lining in the lung and the torso cavity. The infection may start within the chest region and get distributed to other body parts. Other symptoms of pleural mesothelioma cancer include weight loss, severe breathing in trouble, fever, difficulty taking in food, and inflammation of the neck and face areas. It ought to be noted that some people living with the disease don’t experience just about any serious signs or symptoms at all.
One thing I would really like to say is that often before obtaining more laptop or computer memory, look into the machine in which it can be installed. If the machine is running Windows XP, for instance, the particular memory ceiling is 3.25GB. Applying over this would basically constitute just a waste. Be sure that one’s mother board can handle the particular upgrade volume, as well. Interesting blog post.
I’m blown away by the quality of this content! The author has clearly put a huge amount of effort into exploring and arranging the information. It’s exciting to come across an article that not only provides useful information but also keeps the readers captivated from start to finish. Kudos to her for producing such a remarkable piece!
Thanks for your post. What I want to comment on is that when evaluating a good on the net electronics go shopping, look for a internet site with full information on important factors such as the security statement, basic safety details, payment options, along with other terms and also policies. Always take time to browse the help in addition to FAQ sections to get a far better idea of the way the shop is effective, what they can do for you, and ways in which you can use the features.
colour prediction app
Hi, i think that i saw you visited my website thus i came to ?return the favor?.I’m attempting to find things to enhance my web site!I suppose its ok to use a few of your ideas!!
Greetings from Carolina! I’m bored to tears at work so I decided to browse your website on my iphone during lunch break. I enjoy the info you present here and can’t wait to take a look when I get home. I’m surprised at how fast your blog loaded on my phone .. I’m not even using WIFI, just 3G .. Anyways, good blog!
Try 66lottery now
Outstanding post however I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Thank you!
Thanks for your interesting article. Other thing is that mesothelioma is generally a result of the breathing of materials from mesothelioma, which is a dangerous material. Its commonly viewed among laborers in the structure industry that have long exposure to asbestos. It could be caused by living in asbestos protected buildings for a long period of time, Your age plays an important role, and some folks are more vulnerable towards the risk in comparison with others.
Wonderful website. Lots of helpful info here. I?m sending it to a few buddies ans additionally sharing in delicious. And naturally, thanks for your effort!
Thank you for the good writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! However, how can we communicate?
I have been exploring for a little bit for any high-quality articles or blog posts on this kind of area . Exploring in Yahoo I at last stumbled upon this website. Reading this info So i am happy to convey that I’ve an incredibly good uncanny feeling I discovered just what I needed. I most certainly will make certain to don?t forget this web site and give it a look on a constant basis.
colour prediction app
Try 66lottery now
This design is steller! You most certainly know how to keep a reader entertained. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Fantastic job. I really enjoyed what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
Great ? I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs as well as related information ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, website theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Nice task..
CBD products make available a nearby and enjoyable way to sustain the effects of this compound. These gummies fingers on in diverse flavors, potencies, and formulations, providing users with controlled dosing and long-lasting effects. Divers consumers appreciate them as a service to relaxation’, anguish relief. Putting, it’s portentous to consume them responsibly, as effects may pilfer longer to kick in compared to smoking or vaping. Everlastingly voucher dosage guidelines and certify compliance with nearby laws before purchasing or consuming.
Try jalwa game now
hi!,I like your writing so much! share we communicate more about your post on AOL? I need a specialist on this area to solve my problem. Maybe that’s you! Looking forward to see you.
Hi! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good gains. If you know of any please share. Many thanks!
I’ve observed that in the world today, video games are classified as the latest phenomenon with kids of all ages. Many times it may be impossible to drag your family away from the video games. If you want the very best of both worlds, there are various educational games for kids. Thanks for your post.
I am really enjoying the theme/design of your site. Do you ever run into any browser compatibility issues? A number of my blog visitors have complained about my site not working correctly in Explorer but looks great in Opera. Do you have any recommendations to help fix this issue?
Howdy this is kind of of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding experience so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
Currently it appears like Movable Type is the preferred blogging platform available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you’re using on your blog?
Thank you for this article. I’d personally also like to talk about the fact that it can possibly be hard when you find yourself in school and merely starting out to initiate a long credit rating. There are many learners who are simply trying to pull through and have a lengthy or favourable credit history is often a difficult matter to have.
Would you be considering exchanging hyperlinks?
My spouse and I stumbled over here coming from a different web page and thought I should check things out. I like what I see so now i am following you. Look forward to looking over your web page for a second time.
I have really noticed that credit repair activity needs to be conducted with tactics. If not, it’s possible you’ll find yourself destroying your standing. In order to realize your aspirations in fixing your credit score you have to always make sure that from this instant you pay all your monthly dues promptly before their timetabled date. It is really significant on the grounds that by not really accomplishing so, all other methods that you will decide on to improve your credit rank will not be successful. Thanks for expressing your ideas.
I believe that avoiding prepared foods may be the first step to be able to lose weight. They could taste excellent, but highly processed foods possess very little nutritional value, making you eat more just to have enough vitality to get throughout the day. If you are constantly eating these foods, switching to whole grain products and other complex carbohydrates will help you have more power while having less. Good blog post.
Thanks for discussing your ideas. A very important factor is that college students have a choice between government student loan along with a private education loan where it can be easier to choose student loan debt consolidation than over the federal education loan.
I?ll right away grasp your rss as I can not find your email subscription link or e-newsletter service. Do you have any? Kindly allow me understand so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
hentai porn download
It?s really a nice and useful piece of information. I am glad that you shared this helpful information with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Via my notice, shopping for consumer electronics online can for sure be expensive, although there are some principles that you can use to obtain the best discounts. There are constantly ways to obtain discount offers that could make one to possess the best electronic devices products at the lowest prices. Interesting blog post.
I am not sure where you’re getting your information, but good topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or understanding more. Thanks for excellent information I was looking for this information for my mission.
Nice blog right here! Additionally your web site so much up very fast! What host are you using? Can I get your associate link in your host? I want my site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
I’m extremely inspired together with your writing skills as neatly as with the format for your blog. Is that this a paid theme or did you modify it your self? Anyway stay up the nice high quality writing, it is rare to look a nice weblog like this one these days..
Thank you for sharing excellent informations. Your web site is so cool. I’m impressed by the details that you?ve on this blog. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for extra articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the info I already searched all over the place and simply could not come across. What an ideal web-site.
This webpage won’t show up appropriately on my iphone 4 – you may wanna try and repair that
Do you mind if I quote a few of your articles as long as I provide credit and sources back to your website? My website is in the exact same area of interest as yours and my visitors would genuinely benefit from some of the information you provide here. Please let me know if this ok with you. Regards!
Thanks for the tips you are revealing on this site. Another thing I want to say is that getting hold of copies of your credit file in order to examine accuracy of any detail will be the first measures you have to undertake in credit score improvement. You are looking to clear your credit file from detrimental details errors that damage your credit score.
Interesting blog post. Some tips i would like to bring about is that computer memory ought to be purchased in case your computer cannot cope with whatever you do along with it. One can deploy two RAM memory boards of 1GB each, for example, but not one of 1GB and one with 2GB. One should always check the company’s documentation for the PC to make certain what type of ram is required.
whoah this blog is magnificent i love reading your posts. Keep up the good work! You know, lots of people are hunting around for this info, you could help them greatly.
Thanks for the strategies you have discussed here. On top of that, I believe usually there are some factors which really keep your car insurance policy premium decrease. One is, to contemplate buying cars and trucks that are in the good list of car insurance organizations. Cars that happen to be expensive will be more at risk of being lost. Aside from that insurance coverage is also based on the value of your car, so the more pricey it is, then the higher a premium you pay.
Via my research, shopping for electronic devices online may be easily expensive, yet there are some principles that you can use to help you get the best deals. There are often ways to find discount specials that could help make one to hold the best electronic devices products at the lowest prices. Good blog post.
It?s really a great and helpful piece of info. I?m glad that you shared this useful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
I just added this blog to my google reader, excellent stuff. Can’t get enough!
Analysts : Bitcoin experiencing ‘shakeout,’ not end of 4-year cycle
Ethereum Foundation confirm $1.25M to Tornado Cash defense
Rocket Pool’s Ethereum staking service reaches $1B in TVL
Arbitrum whales transfer $18.5M in tokens following $2.3B unlock
Your posts are like a breath of fresh air I appreciate how you tackle difficult topics with grace and empathy
Love this appreciation for great content
This blog serves as a reminder to take care of our mental health and well-being Thank you for promoting a healthier and happier mindset
Wow, I had never thought about it in that way before You have really opened my eyes to a new perspective Keep up the great work!
It’s always a joy to stumble upon content that genuinely makes an impact and leaves you feeling inspired. Keep up the great work!
You have a way of explaining complex topics in a straightforward and easy to understand manner Your posts are always a pleasure to read
I have figured out some points through your site post. One other point I would like to talk about is that there are various games available on the market designed specifically for preschool age youngsters. They involve pattern identification, colors, dogs, and forms. These generally focus on familiarization as opposed to memorization. This will keep children and kids engaged without having a sensation like they are studying. Thanks
Rocket Pool’s Ethereum staking service reaches $1B in TVL
Ethereum Foundation confirm $1.25M to Tornado Cash defense
Does your website have a contact page? I’m having a tough time locating it but, I’d like to send you an e-mail. I’ve got some suggestions for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great blog and I look forward to seeing it develop over time.
I?ve been exploring for a little for any high quality articles or weblog posts in this sort of house . Exploring in Yahoo I finally stumbled upon this website. Reading this information So i am satisfied to convey that I have an incredibly just right uncanny feeling I found out exactly what I needed. I such a lot unquestionably will make sure to do not put out of your mind this website and provides it a look regularly.
no kyc casino
US Bitcoin reserve prompts $370 million in ETF outflows: Farside
Elon Musk’s X eyeing capital raise at $44B valuation: Report
Phantom takes second spot in Apple’s US App Store utilities category
Hello, you used to write great, but the last several posts have been kinda boring? I miss your great writings. Past several posts are just a bit out of track! come on!
Phantom takes second spot in Apple’s US App Store utilities category
This web page does not render correctly on my iphone 4 – you might want to try and repair that
I do believe that a foreclosure can have a major effect on the applicant’s life. Home foreclosures can have a Six to few years negative effect on a applicant’s credit report. Any borrower having applied for home financing or virtually any loans for that matter, knows that your worse credit rating can be, the more difficult it is to have a decent bank loan. In addition, it could possibly affect the borrower’s capability to find a decent place to lease or hire, if that turns into the alternative homes solution. Thanks for your blog post.
I’ve learned newer and more effective things out of your blog post. One other thing I have found is that normally, FSBO sellers are going to reject a person. Remember, they will prefer never to use your services. But if an individual maintain a reliable, professional romance, offering support and remaining in contact for around four to five weeks, you will usually be capable of win an interview. From there, a house listing follows. Thank you
Elon Musk’s X eyeing capital raise at $44B valuation: Report
Trump Opens 300x Leverage Trade After Call with Putin – Is This the Trade of the Century?
Trading Bitcoin’s halving: 3 traders share their thoughts
Analysts : Bitcoin experiencing ‘shakeout,’ not end of 4-year cycle
I have not checked in here for a while because I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are good quality so I guess I will add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Good ? I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs and related information ended up being truly simple to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, web site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Nice task..
Analysts : Bitcoin experiencing ‘shakeout,’ not end of 4-year cycle
I will also like to state that most individuals who find themselves without having health insurance can be students, self-employed and those that are laid-off. More than half of those uninsured are under the age of Thirty five. They do not feel they are wanting health insurance simply because they’re young plus healthy. Their particular income is typically spent on property, food, and entertainment. Lots of people that do work either 100 or part time are not offered insurance via their work so they get along without because of the rising price of health insurance in america. Thanks for the ideas you discuss through this website.
บริการเช่ารถกระเช้า
One other issue is that if you are in a predicament where you will not have a co-signer then you may really want to try to make use of all of your school funding options. You could find many funds and other free college funding that will supply you with funding to help you with college expenses. Thanks for the post.
scissors lift
I will right away grab your rss feed as I can not find your email subscription link or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Please let me know so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
Your webpage does not show up correctly on my i phone – you might wanna try and repair that
My partner and I absolutely love your blog and find many of your post’s to be just what I’m looking for. Would you offer guest writers to write content for you personally? I wouldn’t mind producing a post or elaborating on a number of the subjects you write regarding here. Again, awesome site!
Hey! I just wanted to ask if you ever have any problems with hackers? My last blog (wordpress) was hacked and I ended up losing several weeks of hard work due to no data backup. Do you have any methods to prevent hackers?
Good job!
Buy Drugs
Thanks for your post made here. One thing I’d like to say is most professional areas consider the Bachelor Degree just as the entry level standard for an online certification. Whilst Associate Degrees are a great way to begin with, completing a person’s Bachelors presents you with many entrances to various employment opportunities, there are numerous internet Bachelor Course Programs available through institutions like The University of Phoenix, Intercontinental University Online and Kaplan. Another issue is that many brick and mortar institutions present Online types of their qualifications but commonly for a extensively higher payment than the organizations that specialize in online higher education degree plans.
How to Swap Tokens on ApeSwap: A Complete Guide 2025
How to Use Rhino Bridge for Secure and Fast Crypto Transfers
My partner and I stumbled over here by a different website and thought I should check things out. I like what I see so i am just following you. Look forward to going over your web page yet again.
This helped me a lot.
This is gold, thanks!
I have acquired some new issues from your web-site about pc’s. Another thing I’ve always believed is that computers have become an item that each family must have for some reasons. They provide convenient ways in which to organize households, pay bills, go shopping, study, tune in to music and in many cases watch television shows. An innovative strategy to complete all of these tasks is with a mobile computer. These personal computers are mobile ones, small, effective and easily transportable.
Excellent post. I used to be checking continuously this blog and I am inspired! Extremely useful info specifically the closing section 🙂 I maintain such info much. I was looking for this particular information for a very long time. Thanks and good luck.
Fantastic website. Lots of helpful info here. I?m sending it to some pals ans also sharing in delicious. And naturally, thank you to your effort!
Tornado Cash – Best Crypto Platform for Protects Your Crypto in 2025
Tornado Cash – Best Crypto Platform for Protects Your Crypto in 2025
I really appreciate this post. I have been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You’ve made my day! Thanks again
I have been browsing online more than three hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It is pretty worth enough for me. In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the web will be much more useful than ever before.
How to Use SpookySwap: A Step-by-Step Guide for DeFi Enthusiasts
Valuable info. Lucky me I found your site by accident, and I’m shocked why this accident didn’t happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
Love the tone here.
Very good website you have here but I was curious about if you knew of any discussion boards that cover the same topics talked about here? I’d really love to be a part of community where I can get opinions from other experienced people that share the same interest. If you have any suggestions, please let me know. Thanks!
Audio began playing when I opened up this web page, so irritating!
Your content is so helpful.
Do you mind if I quote a couple of your articles as long as I provide credit and sources back to your blog? My website is in the very same niche as yours and my visitors would really benefit from some of the information you provide here. Please let me know if this okay with you. Thanks!
Scam
You actually make it seem really easy along with your presentation however I to find this matter to be really something which I feel I might never understand. It kind of feels too complicated and extremely wide for me. I am taking a look ahead in your subsequent post, I will try to get the hang of it!
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know so much about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you could do with a few pics to drive the message home a little bit, but instead of that, this is great blog. A fantastic read. I’ll definitely be back.
Another thing I have really noticed is that for many people, low credit score is the reaction of circumstances further than their control. One example is they may are already saddled with illness so they have substantial bills going to collections. It would be due to a job loss or the inability to work. Sometimes divorce proceedings can truly send the finances in the wrong direction. Thank you for sharing your ideas on this blog.
Erectile dysfunction affects as much as 40% of men by age 40. This statistic demonstrates how typical ED treatment has actually become, specifically for those looking to get erectile dysfunction medication and determine if Viagra is right for them. Many guys look for to increase their sexual health and self-confidence by considering the effectiveness of ED medications.
Finding the ideal erectile dysfunction medication can be tricky. You have many alternatives for addressing your sexual health requirements. These consist of prescription ED medications and over-the-counter supplements that work by increasing blood flow.
ED tablets been available in various brands and solutions. Prices vary from $14.99 to $43.99. Alternatives consist of prescription drugs like Viagra and Cialis, which require a prescription. Natural supplements with herbs like Korean ginseng and maca are also available.
Your look for the ideal ED treatment starts here, where you can check out prescription to purchase alternatives, including tadalafil in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Learn more about prescription medications and over-the-counter choices. This understanding will assist you make smart options about handling erectile dysfunction.
Deal with health care pros to discover safe, suitable ED medications, as some might need a prescription in the United States. They can direct you towards treatments that resolve your particular health needs. This approach ensures you get the most effective option for your symptoms of erectile dysfunction.
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction and Treatment Needs
Erectile dysfunction (ED) impacts countless males in the United States, triggering numerous to seek prescription ED treatments. About 30 million males battle to develop and maintain an erection. Understanding ED is important for sexual health and wellness, particularly when thinking about the different online services readily available for treatment.
Typical Causes of ED
Lots of factors can affect male erectile dysfunction and blood flow to the penis, impacting the symptoms of erectile dysfunction. The primary causes include:
Cardiovascular diseases
Diabetes (affecting up to 75% of diabetic males)
Hormonal imbalances can add to the risk of ED and might require particular treatment methods for the treatment of erectile dysfunction, consisting of taking ED medications.
Mental conditions like anxiety and depression
Age-related changes
Signs You May Need ED Treatment
Spotting ED symptoms is essential for getting correct care, especially for men with erectile dysfunction. Look out for these crucial signs:
Persistent problem getting or maintaining an erection might need prescription ED treatments.
Decreased libido may help improve ED sometimes, highlighting the complicated nature of symptoms of erectile dysfunction.
Decreased erectile function during intimate minutes can be a considerable symptom of erectile dysfunction.
Experiencing efficiency stress and anxiety might have an effect on ED.
Effect on Quality of Life
ED can harm your self-confidence, relationships, and mental health, making effective treatment for erectile dysfunction vital, particularly for those with mild to moderate ED. Almost half of men over 40 face some symptoms of ED. It’s essential to attend to these problems and look for medical help.
FDA-Approved Medications for Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED) impacts numerous men. FDA-approved medications use reliable treatment options. These drugs improve blood flow and assistance sexual function for millions.
Popular PDE5 Inhibitors
Three primary prescription alternatives are readily available for ED treatment:
Viagra (sildenafil): Works within 30 minutes after taking the tablet, effective for around 4 hours, however may cause a drop in blood pressure.
Cialis (tadalafil): Can last approximately 36 hours, offering extended treatment windows
Levitra (vardenafil): Begins working around 30 minutes after taking ED tablets and lasts about 5 hours, making it easier to get an erection.
Comparing Key Medications
Each medication provides distinct benefits for dealing with ED. Stendra is another option, working in as low as 15 minutes. Its impacts can last as much as 6 hours.
Your medical professional can help select the very best medication for your health needs.
Generic vs Brand Name Options
Generic versions of these medications can save you cash. They contain the same active ingredients as brand-name drugs used to treat ED. However, generic Viagra is generally more affordable.
Constantly speak to your medical professional about utilizing generic medications. They’ll guarantee it’s ideal for your condition.
These medications work however may have negative effects. Headaches, nasal blockage, and vision changes are common. Talk about threats and advantages with your medical professional before starting any new medication, particularly prescription ED treatments.
Where Can I Buy Erectile Dysfunction Pills: Legal Sources and Options
Finding safe erectile dysfunction (ED) treatment can be challenging. About 30 million U.S. males experience ED. It’s crucial to understand where to purchase medication lawfully to ensure safe and effective erectile dysfunction treatment.
Several reliable sources exist for ED pills that can be obtained without a prescription. These can help restore your confidence and sexual health.
You can get ED medication from different sources that provide treatment online for erectile dysfunction, however be cautious of counterfeit Viagra.
Traditional brick-and-mortar drug stores may also use prescription ED drugs, which can be sold online services that abide by policies.
Online telehealth platforms provide a modern-day technique to exploring treatment for ED.
Licensed online pharmacies provide a practical method to access medications for ED.
Prescription-based digital health care services
Online ED treatment has gained popularity. Many platforms offer virtual consultations with licensed doctor. These services offer practical and personal methods to get prescription ED drugs online for the treatment of erectile dysfunction.
The procedure normally involves obtaining medications for ED through a certified company who can prescribe tablets used to treat ED.
Completing an extensive online health questionnaire is crucial for customized treatment for erectile dysfunction.
Consulting with a doctor is important to determine if Viagra is appropriate for your condition.
Getting a prescribed online medication
Having the prescription delivered directly to your home
When choosing an online pharmacy, inspect their credentials. Look for websites needing valid prescriptions and clear contact details for generic Viagra. Ensure they’re accredited in the United States.
Generic sildenafil expenses between $30-$35 per tablet. It’s a less expensive alternative than brand-name medications like Viagra.
Always work with genuine healthcare providers when looking for second-line treatment for ED. Prevent unauthorized sellers. Your health and wellness come first when treating erectile dysfunction.
Viagra, Over-the-counter ED Meds and Natural Alternatives
Guy typically look for non-prescription alternatives for erectile dysfunction (ED) to get an erection without a prescription, consisting of a glance at OTC Viagra. Over-the-counter tablets and natural alternatives can attend to sexual health concerns. These options offer valuable insights for those wanting to find the best options for ED.
Natural supplements use prospective alternatives for ED treatment. Several key components reveal guarantee in supporting sexual function:
L-arginine: Helps increase blood flow with low dosages, which can be advantageous in the treatment for ED, potentially delivered to your door.
Panax ginseng: May favorably effect sexual efficiency
Propionyl-L-carnitine: Can boost erectile function when combined with other treatments
Care is crucial when considering these supplements. Some bring substantial threats, particularly when considering the effectiveness of ED medications. Yohimbe can trigger severe side effects like increased blood pressure, which might add to ED. The FDA has actually prohibited many non-prescription items declaring to be natural Viagra alternatives that are available nonprescription.
The very best ED treatment involves careful research study and professional medical assistance. About 30 million U.S. guys experience ED. The male enhancement market now goes beyond $3 billion, with lots of choices available, including over-the-counter ED pills.
Constantly consult your healthcare provider before attempting any over-the-counter supplements. They can help evaluate threats and identify the best treatment for you.
How to Safely Purchase ED Medication Online
Buying ED medications online can be tricky. Over half of online ED drugs are phony. It’s essential to understand how to purchase prescription ED drugs safely.
The FDA recommends key steps to safeguard yourself from harmful items. Bewaring and informed is essential when trying to find ED meds online, especially those sold online that declare to treat ED.
Identifying Legitimate Online Pharmacies for Prescription ED
Try to find these signs of a trustworthy online pharmacy:
A certified healthcare provider needs a legitimate prescription online to access medications for ED.
Shows a proven physical address in the United States
Has clear contact information for client support relating to erectile dysfunction drugs.
Offers an online visit with a qualified doctor to talk about ED treatment alternatives, including those that may need a prescription.
Offers transparent rates and medication details for those thinking about prescription ED treatments.
Red Flags of Counterfeit Products
Look out for these warning signs when purchasing ED medications online:
Prices substantially lower than market rates
No prescription requirements
Unsolicited e-mails offering ED meds may often include counterfeit Viagra, so it’s essential to confirm the source.
Websites lacking expert style or reliability may be offering ED medications that are not approved by the Food and Drug Administration.
Promises of wonder remedies or ensured outcomes
Prescription Requirements and Verification
Credible online pharmacies always need a correct prescription. Expect a 15-20 minute online assessment to go over potential effects of ED. Some platforms use 24/7 access and same-day appointments.
Assessment costs vary from $25 to $99. Some services have first-month rates as low as $5.
Your safety comes first, particularly when it concerns developing an unpleasant erection from incorrect use of ED medications. Usage safe and secure, tracked shipping from a validated online pharmacy. Research and confirm before buying to safeguard your health.
Conclusion – Ed Pill
ED affects about 30 million males in the United States, highlighting the need for reliable treatment of erectile dysfunction. It’s a typical concern, and you’re not alone in seeking treatment for ED. Lots of males find efficient ways to enhance their ability to keep an erection.
Your treatment needs to be tailored to your requirements. A lot of ED medications boost blood flow to help with signs. Beware, as some treatments can lower blood pressure, which is a risk of ED and may complicate the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Always consult a doctor first.
Over half of men who seek help find successful treatment choices. FDA-approved prescription medications are the most reliable ED options used to treat erectile dysfunction. Integrating medical treatments with way of life modifications may help improve ED and yield the very best outcomes.
Routine exercise, tension management, and dealing with health problems can enhance sexual function. Your sexual health is important to your total well-being, particularly when you’re unable to get the best treatment for ED. Do not let shame stop you from getting help; many online services provide discreet options for ED treatment.
With different treatment options and professional guidance, consisting of tadalafil in the treatment, you can overcome ED. Do something about it to restore your self-confidence and improve your intimate relationships.
iZiSwap crypto
iZiSwap
Today, we are thrilled to announce that DeepSeek R1 distilled Llama and Qwen models are available through Amazon Bedrock Marketplace and Amazon SageMaker JumpStart. With this launch, you can now release DeepSeek AI’s first-generation frontier model, DeepSeek-R1, together with the distilled variations varying from 1.5 to 70 billion parameters to develop, experiment, and properly scale your generative AI concepts on AWS.
In this post, we show how to begin with DeepSeek-R1 on Amazon Bedrock Marketplace and SageMaker JumpStart. You can follow comparable actions to deploy the distilled variations of the designs as well.
Overview of DeepSeek-R1
DeepSeek-R1 is a large language model (LLM) developed by DeepSeek AI that utilizes reinforcement finding out to enhance thinking abilities through a multi-stage training procedure from a DeepSeek-V3-Base foundation. A key distinguishing feature is its reinforcement knowing (RL) action, which was used to refine the design’s actions beyond the standard pre-training and tweak procedure. By incorporating RL, DeepSeek-R1 can adapt better to user feedback and objectives, eventually enhancing both relevance and clarity. In addition, DeepSeek-R1 uses a chain-of-thought (CoT) approach, suggesting it’s geared up to break down complex inquiries and factor through them in a detailed way. This guided reasoning process permits the design to produce more precise, transparent, and detailed answers. This model combines RL-based fine-tuning with CoT abilities, aiming to produce structured responses while concentrating on interpretability and user interaction. With its comprehensive capabilities DeepSeek-R1 has actually recorded the industry’s attention as a flexible text-generation model that can be integrated into numerous workflows such as representatives, sensible reasoning and data interpretation jobs.
DeepSeek-R1 uses a Mix of Experts (MoE) architecture and is 671 billion parameters in size. The MoE architecture permits activation of 37 billion specifications, allowing effective reasoning by routing questions to the most appropriate expert “clusters.” This method permits the design to focus on various issue domains while maintaining overall effectiveness. DeepSeek-R1 needs a minimum of 800 GB of HBM memory in FP8 format for inference. In this post, we will utilize an ml.p5e.48 xlarge instance to release the model. ml.p5e.48 xlarge features 8 Nvidia H200 GPUs offering 1128 GB of GPU memory.
DeepSeek-R1 distilled models bring the reasoning capabilities of the main R1 design to more effective architectures based on popular open models like Qwen (1.5 B, 7B, 14B, and 32B) and Llama (8B and 70B). Distillation describes a process of training smaller sized, more efficient designs to imitate the habits and reasoning patterns of the bigger DeepSeek-R1 model, using it as an instructor design.
You can deploy DeepSeek-R1 design either through SageMaker JumpStart or Bedrock Marketplace. Because DeepSeek-R1 is an emerging model, we suggest releasing this design with guardrails in place. In this blog, we will utilize Amazon Bedrock Guardrails to introduce safeguards, prevent damaging content, and evaluate models against crucial safety criteria. At the time of composing this blog, for DeepSeek-R1 implementations on SageMaker JumpStart and Bedrock Marketplace, Bedrock Guardrails supports just the ApplyGuardrail API. You can create several guardrails tailored to different usage cases and apply them to the DeepSeek-R1 model, enhancing user experiences and standardizing security controls across your generative AI applications.
Prerequisites
To release the DeepSeek-R1 design, you require access to an ml.p5e circumstances. To inspect if you have quotas for P5e, open the Service Quotas console and under AWS Services, select Amazon SageMaker, and verify you’re using ml.p5e.48 xlarge for endpoint usage. Make certain that you have at least one ml.P5e.48 xlarge instance in the AWS Region you are releasing. To request a limitation increase, produce a limitation boost demand and reach out to your account team.
Because you will be deploying this design with Amazon Bedrock Guardrails, make certain you have the right AWS Identity and Gain Access To Management (IAM) authorizations to utilize Amazon Bedrock Guardrails. For instructions, see Set up approvals to use guardrails for content filtering.
Implementing guardrails with the ApplyGuardrail API
Amazon Bedrock Guardrails permits you to present safeguards, avoid hazardous content, and examine models against crucial safety criteria. You can implement security steps for the DeepSeek-R1 design utilizing the Amazon Bedrock ApplyGuardrail API. This permits you to use guardrails to evaluate user inputs and design reactions deployed on Amazon Bedrock Marketplace and SageMaker JumpStart. You can develop a guardrail using the Amazon Bedrock console or the API. For the example code to create the guardrail, see the GitHub repo.
The general circulation involves the following steps: First, the system receives an input for the model. This input is then processed through the ApplyGuardrail API. If the input passes the guardrail check, it’s sent to the design for reasoning. After getting the model’s output, another guardrail check is applied. If the output passes this final check, it’s returned as the outcome. However, if either the input or output is intervened by the guardrail, a message is returned showing the nature of the intervention and whether it occurred at the input or output stage. The examples showcased in the following sections demonstrate inference using this API.
Deploy DeepSeek-R1 in Amazon Bedrock Marketplace
Amazon Bedrock Marketplace provides you access to over 100 popular, emerging, and specialized structure models (FMs) through Amazon Bedrock. To gain access to DeepSeek-R1 in Amazon Bedrock, total the following actions:
1. On the Amazon Bedrock console, select Model brochure under Foundation designs in the navigation pane.
At the time of composing this post, you can utilize the InvokeModel API to invoke the model. It doesn’t support Converse APIs and other Amazon Bedrock tooling.
2. Filter for DeepSeek as a company and select the DeepSeek-R1 model.
The model detail page provides important details about the design’s abilities, rates structure, and implementation standards. You can find detailed use instructions, consisting of sample API calls and code bits for combination. The design supports numerous text generation tasks, consisting of material creation, code generation, and question answering, utilizing its reinforcement learning optimization and CoT thinking capabilities.
The page likewise includes implementation choices and licensing details to assist you begin with DeepSeek-R1 in your applications.
3. To begin utilizing DeepSeek-R1, pick Deploy.
You will be prompted to set up the release details for DeepSeek-R1. The model ID will be pre-populated.
4. For Endpoint name, enter an endpoint name (in between 1-50 alphanumeric characters).
5. For Variety of instances, go into a variety of instances (between 1-100).
6. For Instance type, choose your instance type. For optimum performance with DeepSeek-R1, a GPU-based circumstances type like ml.p5e.48 xlarge is recommended.
Optionally, you can configure innovative security and facilities settings, including virtual personal cloud (VPC) networking, service role consents, and file encryption settings. For most use cases, the default settings will work well. However, for production deployments, you might wish to review these settings to line up with your organization’s security and compliance requirements.
7. Choose Deploy to begin utilizing the design.
When the implementation is complete, you can check DeepSeek-R1’s abilities straight in the Amazon Bedrock play ground.
8. Choose Open in play area to access an interactive interface where you can experiment with various prompts and adjust model criteria like temperature and optimum length.
When utilizing R1 with Bedrock’s InvokeModel and Playground Console, use DeepSeek’s chat template for optimal results. For example, material for inference.
This is an outstanding method to explore the model’s thinking and text generation capabilities before incorporating it into your applications. The playground offers instant feedback, assisting you comprehend how the design reacts to numerous inputs and letting you fine-tune your prompts for optimal results.
You can rapidly evaluate the design in the play ground through the UI. However, to conjure up the deployed model programmatically with any Amazon Bedrock APIs, you require to get the endpoint ARN.
Run inference utilizing guardrails with the released DeepSeek-R1 endpoint
The following code example shows how to perform inference using a deployed DeepSeek-R1 model through Amazon Bedrock using the invoke_model and ApplyGuardrail API. You can develop a guardrail using the Amazon Bedrock console or the API. For the example code to create the guardrail, see the GitHub repo. After you have developed the guardrail, use the following code to execute guardrails. The script initializes the bedrock_runtime customer, configures reasoning specifications, and sends a demand to create text based upon a user timely.
Deploy DeepSeek-R1 with SageMaker JumpStart
SageMaker JumpStart is an artificial intelligence (ML) center with FMs, built-in algorithms, and prebuilt ML options that you can release with simply a couple of clicks. With SageMaker JumpStart, you can tailor pre-trained models to your usage case, with your information, and release them into production using either the UI or SDK.
Deploying DeepSeek-R1 model through SageMaker JumpStart uses 2 practical techniques: utilizing the instinctive SageMaker JumpStart UI or implementing programmatically through the SageMaker Python SDK. Let’s check out both methods to assist you choose the technique that best matches your needs.
Deploy DeepSeek-R1 through SageMaker JumpStart UI
Complete the following steps to release DeepSeek-R1 utilizing SageMaker JumpStart:
1. On the SageMaker console, choose Studio in the navigation pane.
2. First-time users will be triggered to develop a domain.
3. On the SageMaker Studio console, select JumpStart in the navigation pane.
The model web browser shows available models, with details like the company name and design capabilities.
4. Search for DeepSeek-R1 to view the DeepSeek-R1 model card.
Each design card shows essential details, including:
– Model name
– Provider name
– Task category (for example, Text Generation).
Bedrock Ready badge (if applicable), showing that this model can be registered with Amazon Bedrock, enabling you to use Amazon Bedrock APIs to invoke the model
5. Choose the design card to view the model details page.
The design details page consists of the following details:
– The model name and service provider details.
Deploy button to deploy the design.
About and Notebooks tabs with detailed details
The About tab includes important details, such as:
– Model description.
– License details.
– Technical specifications.
– Usage standards
Before you release the model, it’s recommended to evaluate the model details and license terms to verify compatibility with your use case.
6. Choose Deploy to proceed with implementation.
7. For Endpoint name, use the immediately created name or produce a custom-made one.
8. For Instance type ¸ pick an instance type (default: ml.p5e.48 xlarge).
9. For Initial instance count, go into the variety of circumstances (default: 1).
Selecting suitable instance types and counts is important for expense and performance optimization. Monitor your deployment to change these settings as needed.Under Inference type, Real-time inference is chosen by default. This is optimized for sustained traffic and low latency.
10. Review all setups for precision. For this design, we highly recommend adhering to SageMaker JumpStart default settings and making certain that network seclusion remains in location.
11. Choose Deploy to release the design.
The release process can take several minutes to complete.
When deployment is complete, your endpoint status will change to InService. At this moment, the model is ready to accept reasoning demands through the endpoint. You can monitor the release development on the SageMaker console Endpoints page, which will show relevant metrics and status details. When the deployment is total, you can invoke the model using a SageMaker runtime customer and incorporate it with your applications.
Deploy DeepSeek-R1 utilizing the SageMaker Python SDK
To begin with DeepSeek-R1 utilizing the SageMaker Python SDK, you will need to set up the SageMaker Python SDK and make certain you have the necessary AWS authorizations and environment setup. The following is a detailed code example that shows how to release and use DeepSeek-R1 for reasoning programmatically. The code for deploying the design is offered in the Github here. You can clone the notebook and run from SageMaker Studio.
You can run additional requests against the predictor:
Implement guardrails and run reasoning with your SageMaker JumpStart predictor
Similar to Amazon Bedrock, you can likewise utilize the ApplyGuardrail API with your SageMaker JumpStart predictor. You can produce a guardrail utilizing the Amazon Bedrock console or the API, and implement it as displayed in the following code:
Clean up
To avoid unwanted charges, complete the actions in this section to tidy up your resources.
Delete the Amazon Bedrock Marketplace implementation
If you released the design using Amazon Bedrock Marketplace, total the following steps:
1. On the Amazon Bedrock console, under Foundation designs in the navigation pane, pick Marketplace implementations.
2. In the Managed implementations area, locate the endpoint you wish to erase.
3. Select the endpoint, and on the Actions menu, pick Delete.
4. Verify the endpoint details to make certain you’re deleting the correct implementation: 1. Endpoint name.
2. Model name.
3. Endpoint status
Delete the SageMaker JumpStart predictor
The SageMaker JumpStart design you deployed will sustain costs if you leave it running. Use the following code to erase the endpoint if you desire to stop sustaining charges. For more details, see Delete Endpoints and Resources.
Conclusion
In this post, we explored how you can access and release the DeepSeek-R1 model using Bedrock Marketplace and SageMaker JumpStart. Visit SageMaker JumpStart in SageMaker Studio or Amazon Bedrock Marketplace now to get going. For more details, describe Use Amazon Bedrock tooling with Amazon SageMaker JumpStart designs, SageMaker JumpStart pretrained models, Amazon SageMaker JumpStart Foundation Models, Amazon Bedrock Marketplace, and Beginning with Amazon SageMaker JumpStart.
About the Authors
Vivek Gangasani is a Lead Specialist Solutions Architect for Inference at AWS. He helps emerging generative AI companies develop ingenious services using AWS services and accelerated calculate. Currently, he is concentrated on establishing techniques for fine-tuning and enhancing the reasoning performance of big language designs. In his leisure time, Vivek takes pleasure in treking, seeing films, and trying various foods.
Niithiyn Vijeaswaran is a Generative AI Specialist Solutions Architect with the Third-Party Model Science team at AWS. His area of focus is AWS AI accelerators (AWS Neuron). He holds a Bachelor’s degree in Computer Science and Bioinformatics.
Jonathan Evans is an Expert Solutions Architect working on generative AI with the Third-Party Model Science team at AWS.
Banu Nagasundaram leads item, engineering, and tactical partnerships for Amazon SageMaker JumpStart, SageMaker’s artificial intelligence and generative AI hub. She is passionate about constructing options that help consumers accelerate their AI journey and unlock service worth.
Pornstar
Everything loads super quickly—no delays.
Great post however , I was wanting to know if you could write a litte more on this topic? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit more. Thank you!
Porn site
Great blog post. A few things i would like to contribute is that computer system memory should be purchased when your computer still cannot cope with what you do by using it. One can mount two RAM boards of 1GB each, for instance, but not certainly one of 1GB and one with 2GB. One should always check the maker’s documentation for own PC to be certain what type of storage is required.
Porn site
Excited to see future updates and features!
Porn
Polygon Bridge is a must-have tool in the crypto space.
Viagra
Porn
Wow that was unusual. I just wrote an incredibly long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyways, just wanted to say wonderful blog!
I do not even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was good. I do not know who you are but certainly you’re going to a famous blogger if you are not already 😉 Cheers!
This design is wicked! You most certainly know how to keep a reader amused. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Great job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
Viagra
I like what you guys tend to be up too. This kind of clever work and reporting! Keep up the wonderful works guys I’ve you guys to blogroll.
Thanks alot : ) for your post. I want to say that the cost of car insurance varies from one insurance plan to another, mainly because there are so many different facets which contribute to the overall cost. For instance, the make and model of the car will have a huge bearing on the price tag. A reliable old family auto will have a less expensive premium than the usual flashy racecar.
I can’t express how much I admire the effort the author has put into writing this outstanding piece of content. The clarity of the writing, the depth of analysis, and the abundance of information presented are simply astonishing. Her passion for the subject is apparent, and it has certainly made an impact with me. Thank you, author, for sharing your wisdom and enlightening our lives with this extraordinary article!
Your home is valueble for me. Thanks!?
Sex
I’m amazed, I have to admit. Seldom do I encounter a blog that’s both educative and engaging, and without a doubt, you’ve hit the nail on the head. The problem is an issue that too few people are speaking intelligently about. I am very happy that I came across this in my hunt for something concerning this.
Porn site
arbswap airdrop
Way cool! Some extremely valid points! I appreciate you writing this post and also the rest of the site is also really good.
Thanks for the interesting things you have uncovered in your text. One thing I’d like to touch upon is that FSBO human relationships are built after some time. By releasing yourself to the owners the first weekend break their FSBO can be announced, ahead of the masses start off calling on Mon, you produce a good network. By giving them instruments, educational resources, free reports, and forms, you become a great ally. If you take a personal desire for them plus their circumstance, you build a solid relationship that, on most occasions, pays off in the event the owners opt with an adviser they know as well as trust – preferably you actually.
I was recommended this website by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my trouble. You’re incredible! Thanks!
I?ve read several just right stuff here. Certainly value bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how much attempt you set to create such a great informative site.
This is hands down one of the best articles I’ve read on this topic! The author’s extensive knowledge and passion for the subject are evident in every paragraph. I’m so appreciative for finding this piece as it has enriched my comprehension and ignited my curiosity even further. Thank you, author, for dedicating the time to produce such a outstanding article!
Buy Drugs
You may be able to secure larger loans and enjoy better interest rates by using your home’s equity. Find the best current offers today.
Thanks a bunch for sharing this with all folks you actually recognise what you are speaking approximately! Bookmarked. Kindly additionally visit my website =). We can have a hyperlink change agreement between us!
I do enjoy the way you have presented this difficulty plus it does supply us a lot of fodder for consideration. Nevertheless, from just what I have seen, I only wish when other remarks pile on that men and women continue to be on issue and not get started upon a tirade of some other news of the day. All the same, thank you for this outstanding piece and while I can not necessarily concur with this in totality, I respect your point of view.
Thanks for every other informative website. The place else could I am getting that type of info written in such a perfect means? I have a undertaking that I’m simply now operating on, and I have been on the glance out for such information.
Just want to say your article is as amazing. The clearness in your post is simply excellent and i can assume you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission let me to grab your RSS feed to keep updated with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the gratifying work.
This is how you bridge the future of DeFi.
Scam
Thanks for this excellent article. Yet another thing to mention is that a lot of digital cameras come equipped with any zoom lens that permits more or less of any scene to generally be included simply by ‘zooming’ in and out. All these changes in {focus|focusing|concentration|target|the a**** length will be reflected within the viewfinder and on significant display screen at the back of this camera.
dexguru arbitrum
Loved the 2025 strategies for managing IL—super practical.
I want to to thank you for this excellent read!! I absolutely loved every little bit of it. I’ve got you saved as a favorite to look at new things you post…
Polygon is doing for ETH what L2s are meant to do.
Do you have a spam issue on this blog; I also am a blogger, and I was wanting to know your situation; we have created some nice procedures and we are looking to trade solutions with other folks, why not shoot me an e-mail if interested.
Hi there, just became aware of your blog through Google, and found that it is truly informative. I?m gonna watch out for brussels. I will be grateful if you continue this in future. Many people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Pornstar
polygonbridge
I just added this web site to my google reader, excellent stuff. Can’t get enough!
I’m not that much of a online reader to be honest but your sites really nice, keep it up! I’ll go ahead and bookmark your site to come back in the future. Many thanks
This is the perfect web site for anybody who wants to understand this topic. You understand so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I really would want to…HaHa). You certainly put a brand new spin on a topic that’s been discussed for years. Great stuff, just great!
bridge tokens from bsc to eth
Today, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iphone and tested to see if it can survive a thirty foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is entirely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
portal bridge ecosystem
Hello! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
Decentralization + simplicity = Rhino Bridge gets it right.
This guide made me bullish on Bitcoin DeFi again.
Hey there would you mind stating which blog platform you’re working with? I’m looking to start my own blog soon but I’m having a hard time choosing between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal. The reason I ask is because your layout seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something unique. P.S Sorry for being off-topic but I had to ask!
Oh my goodness! a tremendous article dude. Thanks Nonetheless I am experiencing difficulty with ur rss . Don?t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anyone getting identical rss downside? Anyone who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
Nice post. I be taught something tougher on different blogs everyday. It can always be stimulating to read content from other writers and observe slightly one thing from their store. I?d desire to use some with the content on my weblog whether or not you don?t mind. Natually I?ll give you a hyperlink on your web blog. Thanks for sharing.
Polygon really unlocks Web3 gaming and DeFi potential.
Hello, Neat post. There is an issue along with your site in internet explorer, could test this? IE still is the market leader and a large component to other folks will leave out your wonderful writing due to this problem.
I am really enjoying the theme/design of your site. Do you ever run into any internet browser compatibility problems? A number of my blog audience have complained about my site not working correctly in Explorer but looks great in Safari. Do you have any tips to help fix this issue?
Binance Bridge is my daily DeFi tool.
The root of your writing whilst sounding agreeable in the beginning, did not work properly with me personally after some time. Somewhere within the paragraphs you actually were able to make me a believer unfortunately only for a very short while. I nevertheless have a problem with your jumps in logic and you might do nicely to fill in all those breaks. In the event that you actually can accomplish that, I could certainly end up being amazed.
okmark your weblog and check again here regularly. I am quite sure I will learn a lot of new stuff right here! Best of luck for the next!
I don?t even understand how I stopped up right here, but I believed this publish was once good. I don’t know who you might be but certainly you are going to a well-known blogger for those who aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
I’m really inspired with your writing talents and also with the structure on your blog. Is that this a paid subject matter or did you modify it your self? Either way keep up the excellent high quality writing, it is uncommon to look a great blog like this one nowadays..
It’s appropriate time to make some plans for the future and it is time to be happy. I have read this post and if I could I want to suggest you few interesting things or advice. Maybe you could write next articles referring to this article. I wish to read even more things about it!
One more thing. I believe that there are quite a few travel insurance internet sites of respected companies than enable you to enter your trip details to get you the insurance quotes. You can also purchase this international travel insurance policy on the web by using your current credit card. Everything you need to do is always to enter your own travel specifics and you can be aware of the plans side-by-side. Merely find the package that suits your financial budget and needs after which it use your credit card to buy the idea. Travel insurance on the internet is a good way to begin looking for a reputable company pertaining to international travel insurance. Thanks for expressing your ideas.
That was quick, thanks Rhinobridge!
Looking for a comprehensive Spin Rewriter review that tells you what you need to know? You’ve come to the right place if you’re looking to review Spin Rewriter, the best spinner, and understand its capabilities. After spending considerable time with this popular article-spinning tool, I’m breaking down exactly what it offers, how it performs, and whether it deserves a place in your content creation arsenal, especially in the league as Spin Rewriter. If you’re involved in SEO, affiliate marketing, or any form of content production that requires volume without sacrificing quality, this analysis will help you determine if Spin Rewriter is worth your investment.
What Is Spin Rewriter and How Does It Work?
Spin Rewriter is an advanced article spinning tool that uses ENL Semantic Spinning technology to generate unique content variations from a single source article. But what exactly makes it different from other content spinners on the market?
Unlike basic synonym-swapping tools that often produce barely readable gibberish, Spin Rewriter claims to understand the actual meaning of your text through its Emulated Natural Language technology, making it a great tool for creating unique content. This semantic approach means the Spin Rewriter software analyzes how words relate to each other in context before suggesting alternatives. In practice, this should result in content that maintains readability while passing duplicate content checks, a great thing about Spin Rewriter.
The platform now offers Spin Rewriter AI, its newest iteration incorporating Large Language Model (LLM) technology, setting Spin Rewriter apart from competitors. This update aims to deliver even more human-like rewriting capabilities, with features like paragraph-level rewriting and a Text Humanizer tool that introduces subtle variations to make the content feel genuinely human-written.
Key Features of Spin Rewriter: What Sets It Apart?
When examining the feature set of Spin Rewriter, several capabilities stand out that position it differently from alternative spinning tools in the market:
The ENL Semantic Spinning technology, which Spin Rewriter uses, forms the backbone of Spin Rewriter’s approach to content generation. This technology doesn’t just substitute words with synonyms but actually attempts to understand the meaning and context of sentences, much like how Spin Rewriter is powered by advanced algorithms. For search engine optimization professionals concerned about Google’s increasingly sophisticated content analysis, this semantic understanding is particularly valuable.
Spin Rewriter offers multiple spinning levels, allowing users to rewrite content at the word, phrase, sentence, and paragraph levels, which is especially useful for those who want Spin Rewriter. The paragraph spinning capability is especially useful for creating content that passes comparison tests since it restructures entire blocks of text rather than just changing words.
With the One-Click Rewrite button, you can automatically transform your entire article without manually selecting synonyms. The software also includes a bulk article spinning feature that can process multiple articles simultaneously, making it efficient for those managing large websites or blog networks.
Content Integration and Export Options
Versatility Integration with other tools is another strength of Spin Rewriter when it comes to using the article spinner effectively.
WordPress integration: A dedicated plugin allows direct publishing of spun content to WordPress sites
API access: Developers can incorporate Spin Rewriter’s technology into their own software
Multiple export formats with Spin Rewriter make it easy to create diverse content.: Support for various spintax formats ensures compatibility with other marketing tools
Bulk export to create unique content efficiently.: Generate up to 1,000 unique variations of your article at once
For internet marketers managing multiple properties, these integration capabilities can significantly streamline workflow and content distribution processes.
How to Use Spin Rewriter: A Step-by-Step Guide
If you’re new to article spinning, getting started with Spin Rewriter follows a relatively straightforward process. Here’s how to use Spin Rewriter effectively to spin an article and create unique content using this tool:
Start with quality contentPaste your original article into the Spin Rewriter software editor.
Process the content: Use the One-Click Rewrite button to automatically generate variations
Review and customize your articles you want to spin using Spin Rewriter.: Manually adjust any phrases or words that need fine-tuning
Export your content: Generate multiple unique versions for use across different platforms
What makes Spin Rewriter particularly user-friendly is its intuitive interface, a feature that many Spin Rewriter customers appreciate. The Spin Rewriter dashboard clearly displays all available options, with the main rewriting process broken down into three simple steps. For those who value efficiency, the Spin Rewriter WordPress plugin offers keyboard shortcuts that allow quick navigation between words and phrases during the editing process.
The Text Humanizer feature in Spin Rewriter 11 deserves special mention for its advanced capabilities, making it a standout article spinner. This AI-powered tool adds small imperfections and variations to make the content appear naturally written rather than machine-generated, which can be crucial for avoiding Google’s increasingly sophisticated content filters.
Spin Rewriter Pricing: Is It Worth the Investment?
When evaluating whether to try Spin Rewriter, understanding the pricing structure is essential for determining its value proposition compared to Spin Rewriter alternatives. The Spin Rewriter tool offers several subscription options:
Plan
Price
Key Benefits
Monthly
$47/month for the Spin Rewriter 13 subscription.
Full access, unlimited articles, 1,000,000 AI credits monthly
Yearly
The version of Spin Rewriter currently available is $77/year (currently discounted from $197).
60% savings vs. monthly, plus bonuses including video database access
Lifetime
$497 one-time payment
With Spin Rewriter Gold, you have perpetual access with no recurring fees.
All plans include access to the ENL Semantic Spinning technology and allow unlimited article spinning. The yearly plan offers significant savings compared to the monthly option, especially with their current promotional discount.
A standout offering is the 5-day free trial that lets you test the full feature set before committing financially. Additionally, Spin Rewriter provides a 30-day money-back guarantee, which removes much of the risk from trying the service, making it an attractive option for those who want to get a Spin Rewriter.
For affiliate marketing professionals or content creators who regularly need multiple variations of their articles, the yearly plan often represents the best value, particularly when promotional pricing is available.
Spin Rewriter AI Review: How Good Is The Latest Version?
The latest iteration, Spin Rewriter AI, represents a significant evolution from previous versions, making it a top choice among article spinners. It showcases how Spin Rewriter can help streamline content creation. This update incorporates Large Language Model technology to enhance the rewriting capabilities. But does it deliver better results?
From my testing, the AI version shows marked improvement in creating natural-sounding content. The paragraph-level rewriting is impressive, completely restructuring text while maintaining the core message. This addresses one of the common criticisms of older spinning tools—that they produced technically unique content but were still recognizable as spun.
Some standout AI features include:
Paragraph-Level Rewriting using Spin Rewriter is a powerful feature for content creators who want to spin articles in English.: Complete restructuring of paragraphs while maintaining meaning
SEO Content Co-Pilot is enhanced using Spin Rewriter, the best spinner for content creation. Using Spin Rewriter’s overview, it automatically generates optimized metadata, including titles and descriptions.
Text Humanizer: Makes content undetectable as machine-generated by introducing subtle human-like variations, a key aspect of how Spin Rewriter uses emulated natural language.
Built-In Translator: Spin Rewriter translates generated articles into 30+ languages, enhancing its utility as an article spinner.
Text LocalizerSpin Rewriter uses advanced algorithms to adapt content for specific English-speaking markets (US, UK, Australia, etc.). using the Spin Rewriter tool.
The technology better understands contextual relationships between words, producing more coherent and readable results. For SEO specialists concerned about Google’s quality standards, this advancement represents a meaningful step forward in spinning technology.
Spin Rewriter vs. Quillbot and Other Alternatives
How does Spin Rewriter compare to other popular content spinning and paraphrasing tools like Quillbot, especially regarding user-friendliness and effectiveness as an article spinner? I frequently encounter this question from readers who want to spin their options.
Quillbot focuses primarily on paraphrasing rather than creating multiple content variations, unlike Spin Rewriter, a great article rewriter. It excels at rewriting individual paragraphs or short pieces but lacks the bulk spinning capabilities that Spin Rewriter offers. Spin Rewriter provides more robust functionality for creating large volumes of unique content versions.
Other alternatives like WordAi and Chimp Rewriter also compete in this space. WordAi similarly uses AI technology for spinning but comes at a higher price point. Chimp Rewriter offers a desktop-based alternative with comparable features but lacks some of the cloud-based convenience of Spin Rewriter.
“The difference between basic spinners and advanced tools like Spin Rewriter is analogous to the difference between translation dictionaries and human translators. One substitutes words; the other understands meaning.” – Common perspective among content marketers is that Spin Rewriter is a great tool for efficient content creation.
Spin Rewriter differentiates itself in its balance of user-friendliness, spinning quality, and value, which many users appreciate when they want to use this tool. The interface is more approachable than some competitors, while the technology behind it produces generally superior results to budget alternatives.
Is Spin Rewriter Good for SEO? What You Need to Know
Search engine optimization professionals often ask whether spun content is viable in today’s SEO landscape. The answer requires some nuance.
Google has made it abundantly clear that it values original, high-quality content. Its algorithms have become increasingly sophisticated at detecting low-quality spun content. However, well-spun content that maintains readability and coherence can still be effective, particularly for supporting content and backlink diversification.
Here’s the reality: using poorly spun content across multiple high-visibility sites will likely trigger quality flags. However, Spin Rewriter’s semantic technology produces results that, when properly reviewed and edited, can be indistinguishable from human-written variations, making it a great tool for content creators.
For SEO applications, Spin Rewriter works best when:
You start with high-quality original content to write content that resonates with your audience, and Spin Rewriter can completely generate unique variations of that content.
You use the more advanced spinning features (sentence and paragraph-level rewriting)
You review and edit the output before publishing
You distribute the content thoughtfully across different tiers of sites using the Spin Rewriter WordPress license for seamless integration.
Many users report success using Spin Rewriter for supporting content, tier-two link building, and creating variations for multiple properties, showing the power of Spin Rewriter as an effective article rewriter. The key is using it as a tool to enhance efficiency, not as a complete replacement for quality content creation.
How to Cancel Spin Rewriter If You’re Not Satisfied
While many users find value in Spin Rewriter, it’s important to know how to cancel if the tool doesn’t meet your needs. The cancellation process is straightforward:
Log into your Spin Rewriter account
Navigate to the “My Account” page to get a Spin Rewriter subscription.
Click on the cancellation option
Confirm your cancellation
Alternatively, if you’ve subscribed through PayPal, you can cancel directly from your account by managing your subscription settings. The company claims its cancellation process requires no direct contact with customer service, making it hassle-free, similar to the Spin Rewriter alternative.
It’s worth noting that Spin Rewriter offers a 30-day money-back guarantee in addition to their 5-day free trial, making it a reliable choice for users looking for an article spinner; Spin Rewriter gives users confidence in their investment. You can request a refund within 30 days of purchase if you are unsatisfied with the service or results. This double layer of protection (free trial plus money-back guarantee) significantly reduces the risk of trying the platform. Many users appreciate this customer-friendly approach, demonstrating the company’s confidence in their product’s ability to deliver value.
The platform sends email reminders to those concerned about subscription auto-renewals before charging for the next billing cycle. This gives you adequate time to cancel if you choose not to continue. According to their FAQ section, cancellations are processed immediately without requiring you to speak to a customer service representative or provide extensive justification for your decision.
More Advanced Features of Spin Rewriter
Spin Rewriter includes several advanced features that content writers and power users will appreciate.
Stock Photo Integration: This feature automatically adds relevant, copyright-free images from free stock photo sites to your spun articles, enhancing the quality of content generated by Spin Rewriter, the best spinner.
Mass Export: Spin Rewriter can generate up to 1,000 unique versions of your article with a single click, showcasing its powerful capabilities as an article spinner.
Spintax Format Support: Compatible with all major spintax formats, including second option, Spin Rewriter is easy to integrate into your current workflow.
Bulk Article Rewriting: Spin Rewriter allows you to process multiple articles simultaneously for maximum efficiency as an article spinner.
Spin Rewriter lets you add protected keywords to ensure your content remains unique.: Prevent specific terms from being spun to maintain consistency and branding
Real-World Applications for Spin Rewriter
Many users leverage Spin Rewriter for specific content creation scenarios:
Affiliate Marketing: Create unique product descriptions across multiple affiliate sites
PBN Management is greatly improved by utilizing Spin Rewriter for creating supporting content.: Generate diverse content for private blog networks without obvious duplication
Client SEO Services: Efficiently produce variations for multi-location businesses with the new features of Spin Rewriter.
Content Localization with Spin Rewriter allows you to spin content for various markets.: Adapt existing content for different English-speaking markets
Email Marketing with Spin Rewriter to generate engaging content.: Develop multiple versions of email campaigns for A/B testing
FAQ Section About Spin Rewriter
Does Spin Rewriter create content that passes Copyscape?
Yes, when used properly, content created with Spin Rewriter generally passes Copyscape and other plagiarism checkers, making it a reliable tool for content writers. The ENL Semantic Spinning technology specifically focuses on creating variations that are technically unique while maintaining readability.
Can I use Spin Rewriter for foreign languages?
Spin Rewriter primarily supports English for the spinning process. However, the latest version includes a translation feature that can convert your spun articles into over 30 languages after the spinning process is complete.
Does Spin Rewriter offer an affiliate program?
Yes, Spin Rewriter has an affiliate marketing program that pays 50% commission on all sales you refer. This makes it potentially lucrative for marketers who recommend Spin Rewriter to their audience as a powerful article spinner.
Is Spin Rewriter content safe from Google penalties when you want to spin it?
No tool can guarantee protection from Google penalties. However, Spin Rewriter’s advanced semantic technology creates higher-quality spun content that, when properly edited, is designed to avoid typical footprints that trigger penalties, making it a great tool for SEO professionals.
How does the Spin Rewriter tool access work?
Spin Rewriter provides API access that allows developers to integrate the spinning technology into their own software applications, showcasing how Spin Rewriter can help enhance their projects. This enables customized workflows and automated content spinning within third-party tools.
What are AI credits and how many do I need?
Each Spin Rewriter subscription includes 1,000,000 AI credits monthly, powering the most advanced features. This allocation is sufficient for most users, typically covering 6,000 AI paragraph rewrites, 1,500 auto-generated titles, 800 localized articles, and more.
Pros and Cons of Using Spin Rewriter
Pros:
Advanced ENL semantic understanding creates more readable content
Multiple spinning levels (word, phrase, sentence, paragraph)
User-friendly interface with one-click functionality
WordPress integration and versatile export options
Competitive pricing compared to similar high-end spinning tools
With the comprehensive 5-day free trial and 30-day money-back guarantee, you can get Spin Rewriter without any risk.
Cons:
Even the best spun content typically requires some manual editing
Limited to English language for spinning (though translations available)
Monthly plan is relatively expensive compared to yearly subscription
Learning curve to maximize the more advanced features
Heavily spun content may still encounter SEO issues if not properly reviewed, so reviewing Spin Rewriter’s output is important.
Testimonials From Spin Rewriter Users
“After years of using The Best Spinner, I found Spin Rewriter to be at least 2 years ahead of its time. It’s the ONLY spinner on the market that writes readable spun content with just one click.” – Chris Winters, Digital Marketer
“Spin Rewriter has greatly increased my productivity, allowing me to automatically spin content faster.” Being able to spin the content into unique articles without much rewriting has made my process so much faster and efficient with Spin Rewriter. – Rod Davison, GolferOnFire.com, a proud Spin Rewriter Gold member.
Conclusion: Is Spin Rewriter Worth It in 2025?
In this comprehensive Spin Rewriter review, we’ve examined everything from basic functionality to advanced features and real-world applications, including how Spin Rewriter prevents content duplication. The tool represents one of the more sophisticated options in the article spinning category, particularly with its latest AI-powered iteration, and Spin Rewriter is a powerful tool for content creators.
For content creators, SEO professionals, and affiliate marketers who regularly need to produce multiple variations of quality content, Spin Rewriter offers a compelling solution to spin an article effectively. The semantic understanding technology produces results that are notably better than basic synonym-replacement spinners, while maintaining a user-friendly interface and reasonable price point.
The 5-day free trial makes it easy to test Spin Rewriter before committing, allowing you to determine if it meets your specific content needs, just like about Spin Rewriter. Whether you’re managing multiple blogs, building backlink networks, or simply looking to repurpose existing content efficiently, this tool provides features that can significantly streamline your workflow.
Ultimately, Spin Rewriter works best as part of a balanced content strategy—not as a complete replacement for original writing, but as a powerful efficiency tool for creating variations and supporting content at scale.
Magnificent beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your web site, how can i subscribe for a blog web site? The account helped me a applicable deal. I were a little bit familiar of this your broadcast offered vivid clear concept
Hello There. I found your blog using msn. This is an extremely well written article. I?ll be sure to bookmark it and return to read more of your useful information. Thanks for the post. I will definitely comeback.
I can’t believe how amazing this article is! The author has done a tremendous job of conveying the information in an compelling and informative manner. I can’t thank her enough for providing such precious insights that have undoubtedly enlightened my understanding in this topic. Kudos to him for producing such a work of art!
It?s actually a nice and useful piece of info. I?m glad that you shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
We stumbled over here coming from a different web address and thought I may as well check things out. I like what I see so i am just following you. Look forward to looking over your web page again.
Hi there! Quick question that’s entirely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My web site looks weird when viewing from my iphone 4. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to resolve this problem. If you have any suggestions, please share. With thanks!
Pornstar
Porn
Viagra
F*ckin? tremendous things here. I am very glad to see your post. Thanks a lot and i am looking forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
Heya i?m for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It truly useful & it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and help others like you helped me.
The subsequent time I read a blog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as a lot as this one. I imply, I do know it was my choice to read, but I actually thought youd have one thing interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could repair in case you werent too busy searching for attention.
You made some first rate points there. I seemed on the web for the problem and located most individuals will associate with with your website.
Hi! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone! Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the fantastic work!
Interesting article. It is unfortunate that over the last ten years, the travel industry has already been able to to handle terrorism, SARS, tsunamis, bird flu virus, swine flu, as well as the first ever entire global downturn. Through everything the industry has really proven to be strong, resilient and dynamic, finding new tips on how to deal with hardship. There are always fresh challenges and opportunity to which the sector must again adapt and react.
I have seen a great deal of useful issues on your web page about pc’s. However, I’ve the view that laptops are still not quite powerful more than enough to be a wise decision if you typically do projects that require a lot of power, for example video enhancing. But for web surfing, microsoft word processing, and majority of other common computer work they are okay, provided you never mind small screen size. Many thanks for sharing your thinking.
Hello there! Quick question that’s completely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My weblog looks weird when browsing from my iphone. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to correct this problem. If you have any recommendations, please share. Cheers!
Oh my goodness! I’m in awe of the author’s writing skills and capability to convey complicated concepts in a concise and clear manner. This article is a real treasure that earns all the accolades it can get. Thank you so much, author, for providing your wisdom and offering us with such a priceless treasure. I’m truly grateful!
F*ckin? tremendous issues here. I?m very satisfied to see your article. Thanks a lot and i’m taking a look forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
hello!,I love your writing so so much! percentage we keep in touch more about your article on AOL? I need an expert in this area to unravel my problem. May be that’s you! Looking forward to look you.
In line with my research, after a the foreclosure home is offered at a bidding, it is common for that borrower in order to still have the remaining balance on the mortgage. There are many creditors who try and have all rates and liens repaid by the upcoming buyer. Even so, depending on specific programs, laws, and state guidelines there may be a number of loans which aren’t easily handled through the shift of financial products. Therefore, the obligation still lies on the client that has got his or her property foreclosed on. Many thanks sharing your opinions on this site.
Thanks for your write-up. One other thing is when you are marketing your property alone, one of the difficulties you need to be cognizant of upfront is just how to deal with property inspection reviews. As a FSBO vendor, the key towards successfully switching your property and saving money upon real estate agent income is awareness. The more you realize, the smoother your sales effort will be. One area where this is particularly significant is assessments.
I think other web-site proprietors should take this website as an model, very clean and fantastic user genial style and design, let alone the content. You are an expert in this topic!
Hello would you mind letting me know which webhost you’re working with? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 completely different internet browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot faster then most. Can you recommend a good hosting provider at a honest price? Cheers, I appreciate it!
F*ckin? remarkable things here. I?m very glad to see your article. Thanks a lot and i’m looking forward to contact you. Will you please drop me a mail?
Good post made here. One thing I would really like to say is always that most professional fields consider the Bachelor Degree like thejust like the entry level requirement for an online college degree. Even though Associate Certifications are a great way to get started on, completing your own Bachelors starts up many good opportunities to various professions, there are numerous internet Bachelor Course Programs available by institutions like The University of Phoenix, Intercontinental University Online and Kaplan. Another thing is that many brick and mortar institutions give Online editions of their college diplomas but generally for a extensively higher charge than the providers that specialize in online college degree programs.
What an informative and thoroughly-researched article! The author’s attention to detail and capability to present intricate ideas in a comprehensible manner is truly praiseworthy. I’m thoroughly enthralled by the breadth of knowledge showcased in this piece. Thank you, author, for providing your expertise with us. This article has been a game-changer!
I have been surfing online more than three hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It?s pretty worth enough for me. In my view, if all web owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the web will be much more useful than ever before.
Hey there! Would you mind if I share your blog with my zynga group? There’s a lot of people that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Cheers
You really make it seem really easy together with your presentation but I find this topic to be actually one thing which I believe I would by no means understand. It kind of feels too complex and very huge for me. I am having a look forward in your subsequent post, I?ll try to get the hold of it!
As I web-site possessor I believe the content matter here is rattling wonderful , appreciate it for your hard work. You should keep it up forever! Good Luck.
Thanks for the useful information on credit repair on this excellent site. The thing I would offer as advice to people is to give up the particular mentality that they may buy at this point and fork out later. Being a society most people tend to do that for many factors. This includes vacations, furniture, plus items we wish. However, it is advisable to separate a person’s wants from the needs. While you’re working to improve your credit score you have to make some sacrifices. For example it is possible to shop online to save cash or you can visit second hand outlets instead of high-priced department stores pertaining to clothing.
Hi! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting fed up of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at options for another platform. I would be great if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
One other issue is when you are in a problem where you will not have a co-signer then you may really want to try to wear out all of your financial aid options. You will find many grants and other scholarships and grants that will present you with finances that can help with institution expenses. Many thanks for the post.
Aw, this was a very nice post. In thought I would like to put in writing like this additionally ? taking time and precise effort to make an excellent article? however what can I say? I procrastinate alot and in no way seem to get one thing done.
I love your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz respond as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to know where u got this from. many thanks
Keep up the great work
Thanks for your intriguing article. Other thing is that mesothelioma cancer is generally caused by the breathing of fibers from asbestos fiber, which is a very toxic material. It can be commonly viewed among staff in the construction industry who’ve long contact with asbestos. It could be caused by living in asbestos protected buildings for some time of time, Genes plays a crucial role, and some folks are more vulnerable for the risk as compared with others.
Pretty great post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to mention that I have truly loved surfing around your weblog posts. In any case I?ll be subscribing to your rss feed and I’m hoping you write again very soon!
Good article. It’s very unfortunate that over the last decade, the travel industry has had to handle terrorism, SARS, tsunamis, flu virus, swine flu, as well as the first ever real global downturn. Through all of it the industry has proven to be powerful, resilient as well as dynamic, acquiring new ways to deal with hardship. There are often fresh problems and chance to which the industry must once more adapt and act in response.
Hello there! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting tired of WordPress because I’ve had issues with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Right now it looks like WordPress is the preferred blogging platform available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
Heya i am for the first time here. I found this board and I in finding It truly helpful & it helped me out much. I am hoping to provide one thing again and aid others such as you helped me.
豚に真珠
As I web site possessor I believe the content material here is rattling magnificent , appreciate it for your efforts. You should keep it up forever! Best of luck.
voyeur
Thank you for another informative web site. Where else could I get that type of information written in such an ideal way? I’ve a project that I’m just now working on, and I’ve been on the look out for such information.
I am so happy to read this. This is the type of manual that needs to be given and not the random misinformation that is at the other blogs. Appreciate your sharing this best doc.
Thanks for your posting. Another thing is that being photographer requires not only problem in capturing award-winning photographs and also hardships in getting the best digital camera suited to your requirements and most especially challenges in maintaining the quality of your camera. That is very true and obvious for those photography enthusiasts that are straight into capturing the actual nature’s fascinating scenes : the mountains, the particular forests, the particular wild or perhaps the seas. Visiting these adventurous places surely requires a digicam that can live up to the wild’s harsh setting.
This website is known as a walk-by way of for all the data you wanted about this and didn?t know who to ask. Glimpse right here, and you?ll positively discover it.
Wow that was unusual. I just wrote an really long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t appear. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyway, just wanted to say wonderful blog!
I’m really inspired together with your writing talents as neatly as with the format for your blog. Is that this a paid subject or did you customize it your self? Anyway keep up the nice high quality writing, it is uncommon to look a great weblog like this one these days..
I have noticed that over the course of making a relationship with real estate managers, you’ll be able to come to understand that, in every single real estate exchange, a payment is paid. Eventually, FSBO sellers do not “save” the percentage. Rather, they fight to earn the commission simply by doing a agent’s job. In doing this, they spend their money plus time to conduct, as best they’re able to, the duties of an realtor. Those assignments include disclosing the home through marketing, showing the home to all buyers, making a sense of buyer urgency in order to make prompt an offer, scheduling home inspections, handling qualification check ups with the bank, supervising fixes, and facilitating the closing.
whoah this weblog is excellent i really like studying your posts. Stay up the great paintings! You know, a lot of individuals are searching round for this info, you can aid them greatly.
I enjoy what you guys tend to be up too. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the awesome works guys I’ve added you guys to blogroll.
Wonderful beat ! I wish to apprentice while you amend your web site, how could i subscribe for a blog website? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear concept
Its like you read my mind! You seem to know so much about this, like you wrote the book in it or something. I think that you can do with some pics to drive the message home a bit, but instead of that, this is great blog. An excellent read. I will definitely be back.
I enjoy what you guys are usually up too. This sort of clever work and reporting! Keep up the awesome works guys I’ve included you guys to blogroll.
I have come to understand that fees for on-line degree pros tend to be a great value. For instance a full Bachelors Degree in Communication in the University of Phoenix Online consists of Sixty credits at $515/credit or $30,900. Also American Intercontinental University Online makes available Bachelors of Business Administration with a overall education course feature of 180 units and a cost of $30,560. Online degree learning has made taking your degree far less difficult because you can earn your current degree from the comfort of your abode and when you finish from work. Thanks for all the tips I have really learned through your blog.
Hello! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I genuinely enjoy reading your blog posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same subjects? Thanks a lot!
Hey would you mind letting me know which webhost you’re utilizing? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 completely different web browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot quicker then most. Can you recommend a good internet hosting provider at a fair price? Many thanks, I appreciate it!
Great write-up, I?m normal visitor of one?s web site, maintain up the nice operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
Thanks for the posting. I have often observed that a majority of people are eager to lose weight simply because they wish to look slim as well as attractive. However, they do not often realize that there are additional benefits for losing weight in addition. Doctors declare that fat people suffer from a variety of illnesses that can be instantly attributed to their excess weight. The great thing is that people who definitely are overweight as well as suffering from numerous diseases can reduce the severity of the illnesses by means of losing weight. You’ll be able to see a slow but identifiable improvement in health as soon as even a bit of a amount of fat loss is reached.
I’m amazed, I have to admit. Rarely do I come across a blog that’s both educative and engaging, and without a doubt, you’ve hit the nail on the head. The issue is something that too few men and women are speaking intelligently about. Now i’m very happy I stumbled across this during my hunt for something relating to this.
I need to to thank you for this great read!! I absolutely loved every bit of it. I have you book-marked to look at new things you post…
Great information. Lucky me I ran across your website by chance (stumbleupon). I have bookmarked it for later!
Hi! I could have sworn I’ve visited this site before but after looking at some of the articles I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely pleased I discovered it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back frequently!
The next time I read a blog, Hopefully it won’t fail me just as much as this one. I mean, I know it was my choice to read, nonetheless I actually thought you’d have something interesting to talk about. All I hear is a bunch of whining about something that you could fix if you were not too busy searching for attention.
Thank you for another fantastic post. Where else could anybody get that kind of information in such an ideal way of writing? I have a presentation next week, and I am on the look for such info.
Good post. I learn something new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon everyday. It will always be useful to read articles from other authors and practice a little something from other web sites.
Thanks for your publication. What I want to say is that when you are evaluating a good internet electronics store, look for a web site with full information on important factors such as the level of privacy statement, protection details, any payment options, along with other terms plus policies. Continually take time to investigate the help in addition to FAQ segments to get a greater idea of how a shop is effective, what they are able to do for you, and how you can make use of the features.
I don?t even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was good. I don’t know who you are but definitely you’re going to a famous blogger if you aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
Pretty! This was an incredibly wonderful post. Many thanks for providing this information.
cialis canada pharmacy no prescription required [url=https://tadalaccess.com/#]Tadal Access[/url] mantra 10 tadalafil tablets
Hi! Someone in my Facebook group shared this site with us so I came to give it a look. I’m definitely enjoying the information. I’m book-marking and will be tweeting this to my followers! Superb blog and fantastic style and design.
I figured out more interesting things on this weight loss issue. Just one issue is a good nutrition is especially vital while dieting. A tremendous reduction in bad foods, sugary ingredients, fried foods, sweet foods, red meat, and whitened flour products can be necessary. Having wastes organisms, and contaminants may prevent targets for losing belly fat. While certain drugs in the short term solve the matter, the unpleasant side effects aren’t worth it, and in addition they never supply more than a short lived solution. It is a known proven fact that 95 of diet plans fail. Thanks for sharing your opinions on this website.
Hello! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any suggestions?
My spouse and I absolutely love your blog and find the majority of your post’s to be what precisely I’m looking for. can you offer guest writers to write content for yourself? I wouldn’t mind composing a post or elaborating on most of the subjects you write about here. Again, awesome web log!
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..extra wait .. ?
Hey! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any tips?
I wish to get across my admiration for your kindness supporting those people who must have help with this one field. Your personal commitment to getting the message all through had become really insightful and has constantly made folks just like me to attain their desired goals. Your new useful tutorial signifies a lot a person like me and extremely more to my colleagues. Regards; from each one of us.
One thing is that if you find yourself searching for a student loan you may find that you’ll want a co-signer. There are many scenarios where this is true because you might discover that you do not possess a past credit standing so the financial institution will require you have someone cosign the loan for you. Good post.
Excellent read, I just passed this onto a friend who was doing some research on that. And he actually bought me lunch since I found it for him smile So let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch!
Such a helpful resource.
Excellent blog! Do you have any recommendations for aspiring writers? I’m hoping to start my own website soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you advise starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many options out there that I’m totally confused .. Any suggestions? Appreciate it!
You could certainly see your skills within the work you write. The world hopes for even more passionate writers such as you who are not afraid to mention how they believe. All the time follow your heart.
More content pieces like this would make the internet better.
Thanks a lot for sharing this with all folks you really understand what you are speaking approximately! Bookmarked. Kindly additionally consult with my web site =). We may have a hyperlink alternate arrangement among us!
A motivating discussion is definitely worth comment. There’s no doubt that that you need to write more about this issue, it might not be a taboo matter but generally folks don’t discuss such subjects. To the next! All the best.
The next time I learn a weblog, I hope that it doesnt disappoint me as a lot as this one. I imply, I do know it was my option to read, however I truly thought youd have one thing interesting to say. All I hear is a bunch of whining about one thing that you can fix if you happen to werent too busy looking for attention.
This is a topic that’s close to my heart… Cheers! Exactly where are your contact details though?
Thanks for posting. It’s a solid effort.
I discovered useful points from this.
What i do not understood is actually how you are now not really much more neatly-preferred than you might be now. You’re so intelligent. You already know thus significantly in relation to this topic, made me in my view believe it from so many various angles. Its like men and women don’t seem to be interested unless it?s one thing to do with Woman gaga! Your own stuffs excellent. All the time deal with it up!
I have seen that intelligent real estate agents almost everywhere are getting set to FSBO ***********. They are realizing that it’s in addition to placing a poster in the front yard. It’s really pertaining to building associations with these vendors who later will become customers. So, if you give your time and effort to serving these vendors go it alone : the “Law associated with Reciprocity” kicks in. Interesting blog post.
Today, taking into consideration the fast life style that everyone is having, credit cards have a huge demand throughout the economy. Persons from every arena are using the credit card and people who are not using the credit card have made up their minds to apply for even one. Thanks for revealing your ideas in credit cards.
This is a good tip especially to those fresh to the blogosphere. Simple but very accurate information… Thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
I was very happy to search out this web-site.I wanted to thanks to your time for this glorious read!! I positively enjoying every little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to take a look at new stuff you weblog post.
Good post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon everyday. It will always be exciting to read content from other writers and use something from other websites.
Can I simply say what a relief to find somebody who truly knows what they are discussing on the internet. You definitely realize how to bring a problem to light and make it important. A lot more people ought to read this and understand this side of the story. I can’t believe you are not more popular given that you definitely have the gift.
I would like to thank you for the efforts you’ve put in writing this website. I am hoping to check out the same high-grade blog posts from you later on as well. In truth, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own site now 😉
Good day! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading through this post reminds me of my previous room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this write-up to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
I used to be able to find good advice from your blog posts.
It?s actually a nice and helpful piece of info. I?m happy that you simply shared this useful info with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
One other issue is when you are in a situation where you do not have a co-signer then you may really need to try to exhaust all of your money for college options. You can find many funds and other scholarships or grants that will ensure that you get funds to assist with education expenses. Thank you for the post.
Hello! I just wish to offer you a huge thumbs up for the great information you have got right here on this post. I will be returning to your website for more soon.
Thanks for your thoughts. One thing I’ve got noticed is the fact banks and also financial institutions are aware of the spending habits of consumers while also understand that most of the people max outside their cards around the getaways. They smartly take advantage of this kind of fact and begin flooding the inbox along with snail-mail box along with hundreds of no interest APR credit card offers soon after the holiday season comes to an end. Knowing that for anyone who is like 98 of American open public, you’ll soar at the chance to consolidate credit card debt and shift balances to 0 APR credit cards.
Hello! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be okay. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new updates.
Thanks for making me to get new thoughts about computer systems. I also have belief that certain of the best ways to maintain your notebook computer in excellent condition is by using a hard plastic-type material case, and also shell, that fits over the top of the computer. A lot of these protective gear are model unique since they are manufactured to fit perfectly across the natural casing. You can buy all of them directly from the owner, or from third party places if they are designed for your notebook computer, however only a few laptop could have a spend on the market. Once again, thanks for your guidelines.
This article is absolutely incredible! The author has done a fantastic job of delivering the information in an captivating and enlightening manner. I can’t thank him enough for sharing such valuable insights that have definitely enriched my understanding in this topic. Bravo to her for creating such a work of art!
I have seen that car insurance providers know the automobiles which are liable to accidents along with risks. In addition they know what sort of cars are given to higher risk plus the higher risk they’ve got the higher the particular premium amount. Understanding the basic basics of car insurance just might help you choose the right sort of insurance policy that can take care of the needs you have in case you happen to be involved in an accident. Thank you for sharing a ideas on the blog.
Someone essentially help to make seriously posts I would state. This is the first time I frequented your website page and thus far? I amazed with the research you made to create this particular publish amazing. Excellent job!
Thanks for the tips on credit repair on this amazing site. Some tips i would advice people is usually to give up this mentality they can buy currently and fork out later. As being a society most people tend to do this for many things. This includes getaways, furniture, and items we would like. However, you’ll want to separate your current wants from the needs. While you’re working to fix your credit score actually you need some sacrifices. For example you are able to shop online to save money or you can click on second hand merchants instead of high-priced department stores to get clothing.
One thing is that if you find yourself searching for a student loan you may find that you will want a cosigner. There are many conditions where this is correct because you might find that you do not possess a past credit standing so the mortgage lender will require that you’ve got someone cosign the loan for you. Interesting post.
I have learn several good stuff here. Certainly value bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how a lot attempt you put to create this type of great informative site.
Simply want to say your article is as amazing. The clearness for your submit is simply excellent and that i could suppose you are an expert in this subject. Well along with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep up to date with imminent post. Thank you 1,000,000 and please carry on the rewarding work.
certainly like your web site but you have to check the spelling on several of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very bothersome to inform the truth then again I will surely come back again.
One thing is the fact one of the most prevalent incentives for making use of your credit card is a cash-back or maybe rebate provision. Generally, you get 1-5 back in various expenditures. Depending on the credit card, you may get 1 returning on most expenses, and 5 back again on expenses made in convenience stores, filling stations, grocery stores and also ‘member merchants’.
More content pieces like this would make the internet a better place.
I appreciate, cause I found just what I was looking for. You have ended my 4 day long hunt! God Bless you man. Have a great day. Bye
I used to be very pleased to search out this net-site.I wished to thanks in your time for this excellent read!! I definitely enjoying each little little bit of it and I’ve you bookmarked to check out new stuff you weblog post.
I believe that a foreclosed can have a significant effect on the client’s life. Home foreclosures can have a 7 to decade negative affect on a client’s credit report. A borrower who’s applied for a mortgage or any kind of loans for that matter, knows that the actual worse credit rating will be, the more tough it is to have a decent personal loan. In addition, it could possibly affect any borrower’s power to find a good place to lease or hire, if that gets to be the alternative property solution. Interesting blog post.
Heya i am for the first time here. I came across this board and I in finding It truly helpful & it helped me out much. I am hoping to provide something back and aid others such as you aided me.
This is the kind of content I find helpful.
I discovered useful points from this.
Good day! I just would like to give a huge thumbs up for the nice data you might have right here on this post. I will be coming back to your weblog for extra soon.
Whats up very cool site!! Guy .. Beautiful .. Wonderful .. I’ll bookmark your blog and take the feeds also?I’m satisfied to seek out numerous useful info right here in the submit, we want develop more techniques in this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
I?m impressed, I have to say. Actually hardly ever do I encounter a blog that?s each educative and entertaining, and let me tell you, you’ve gotten hit the nail on the head. Your idea is outstanding; the problem is something that not enough persons are speaking intelligently about. I’m very joyful that I stumbled across this in my search for something regarding this.
Very well explained. Thanks a lot!
This is the kind of content I truly appreciate.
I’m not sure exactly why but this website is loading extremely slow for me. Is anyone else having this issue or is it a problem on my end? I’ll check back later on and see if the problem still exists.
너무 현실적인 조언이라 바로 실천해보고 싶어졌어요.
More articles like this would make the online space richer.
Such a informative read.
Hey, you used to write magnificent, but the last few posts have been kinda boring? I miss your super writings. Past several posts are just a bit out of track! come on!
Hello! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this website? I’m getting tired of WordPress because I’ve had problems with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be awesome if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
I truly liked the way this was explained.
This submission is excellent.
Thanks for these guidelines. One thing I also believe is that often credit cards giving a 0 apr often bait consumers with zero rate, instant endorsement and easy online balance transfers, nevertheless beware of the real factor that can void your current 0 easy street annual percentage rate plus throw you out into the terrible house quick.
More content pieces like this would make the internet richer.
I think this is among the most important information for me. And i am glad reading your article. But should remark on some general things, The site style is great, the articles is really great : D. Good job, cheers
This is the kind of post I look for.
Thanks for putting this up. It’s top quality.
With havin so much content do you ever run into any issues of plagorism or copyright violation? My website has a lot of exclusive content I’ve either written myself or outsourced but it appears a lot of it is popping it up all over the internet without my permission. Do you know any methods to help protect against content from being ripped off? I’d truly appreciate it.
I truly admired the style this was presented.
Such a informative resource.
A formidable share, I just given this onto a colleague who was doing slightly analysis on this. And he in actual fact purchased me breakfast because I discovered it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the deal with! However yeah Thnkx for spending the time to discuss this, I really feel strongly about it and love reading more on this topic. If potential, as you change into experience, would you thoughts updating your weblog with extra particulars? It is extremely useful for me. Large thumb up for this weblog submit!
Hello there! This blog post couldn’t be written much better! Looking through this post reminds me of my previous roommate! He always kept talking about this. I am going to send this article to him. Fairly certain he will have a great read. Thanks for sharing!
Hi my friend! I want to say that this article is awesome, nice written and include approximately all vital infos. I would like to see more posts like this.
I’ve learned many important things by means of your post. I would also like to state that there will be a situation in which you will have a loan and do not need a co-signer such as a Fed Student Aid Loan. However, if you are getting a borrowing arrangement through a conventional financial institution then you need to be able to have a cosigner ready to allow you to. The lenders can base that decision using a few elements but the greatest will be your credit standing. There are some lenders that will furthermore look at your work history and choose based on that but in many instances it will depend on your rating.
As I web site possessor I believe the content matter here is rattling wonderful , appreciate it for your hard work. You should keep it up forever! Best of luck.
I absolutely admired the manner this was explained.
Thanks for the a new challenge you have discovered in your article. One thing I want to reply to is that FSBO relationships are built eventually. By presenting yourself to owners the first weekend their FSBO is usually announced, prior to masses start out calling on Wednesday, you develop a good relationship. By sending them equipment, educational elements, free records, and forms, you become a great ally. By taking a personal desire for them along with their circumstances, you generate a solid interconnection that, many times, pays off in the event the owners opt with a representative they know along with trust — preferably you.
I discovered useful points from this.
I learned a lot from this.
Medyum Haluk Hoca’ya başvurduktan sonra üzerimdeki kötü enerjiler dağıldı. Vefk hazırlığı ve dua ritüelleriyle ruhen de rahatladım. Gönül rahatlığıyla tavsiye ediyorum.
Such a beneficial bit of content.
In my opinion that a foreclosure can have a major effect on the borrower’s life. Real estate foreclosures can have a 7 to a decade negative impact on a client’s credit report. A borrower who have applied for a mortgage or virtually any loans for example, knows that a worse credit rating is actually, the more complicated it is to acquire a decent bank loan. In addition, it could affect any borrower’s capability to find a good place to lease or rent, if that gets to be the alternative houses solution. Good blog post.
great points altogether, you just gained a new reader. What would you suggest in regards to your post that you made a few days ago? Any positive?
Oh my goodness! a tremendous article dude. Thanks However I’m experiencing issue with ur rss . Don?t know why Unable to subscribe to it. Is there anybody getting an identical rss drawback? Anyone who knows kindly respond. Thnkx
I really appreciated the manner this was presented.
More articles like this would make the internet a better place.
Thanks for the helpful write-up. It is also my opinion that mesothelioma cancer has an incredibly long latency time period, which means that symptoms of the disease might not emerge until eventually 30 to 50 years after the primary exposure to asbestos fiber. Pleural mesothelioma, that’s the most common type and is affecting the area across the lungs, might result in shortness of breath, chest muscles pains, and a persistent cough, which may lead to coughing up blood.
Have you ever considered writing an ebook or guest authoring on other sites? I have a blog based on the same subjects you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my audience would enjoy your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an e mail.
Pretty! This has been an extremely wonderful article. Thanks for providing this info.
I’ll gladly recommend this.
I’ll definitely bookmark this page.
I have mastered some important matters through your blog post post. One other point I would like to talk about is that there are many games available and which are designed specifically for preschool age little ones. They include pattern acknowledgement, colors, wildlife, and models. These often focus on familiarization in lieu of memorization. This will keep a child occupied without feeling like they are studying. Thanks
Good blog post. A few things i would like to contribute is that laptop memory should be purchased if the computer can’t cope with whatever you do with it. One can put in two random access memory boards having 1GB each, by way of example, but not certainly one of 1GB and one having 2GB. One should look for the car maker’s documentation for one’s PC to be certain what type of memory space is needed.
I need to to thank you for this fantastic read!! I definitely enjoyed every little bit of it. I’ve got you bookmarked to look at new things you post…
글이 너무 이해하기 쉬웠어요!
Impressive content. Subscribed!
Thanks for posting. It’s a solid effort.
One thing I want to say is that before buying more computer system memory, consider the machine in which it will be installed. When the machine is definitely running Windows XP, for instance, the memory ceiling is 3.25GB. Installing a lot more than this would simply constitute just a waste. Make certain that one’s mother board can handle the particular upgrade volume, as well. Great blog post.
Fantastic beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your site, how can i subscribe for a blog website? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear idea
It’s hard to find experienced people on this topic, however, you seem like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
That is a great tip particularly to those new to the blogosphere. Short but very accurate information… Many thanks for sharing this one. A must read article.
This is the kind of post I look for.
More blogs like this would make the online space richer.
May I just say what a relief to uncover an individual who genuinely knows what they’re talking about on the internet. You actually realize how to bring a problem to light and make it important. More and more people ought to look at this and understand this side of your story. I was surprised that you’re not more popular since you definitely possess the gift.
The detail in this article is praiseworthy.
This submission is amazing.
Excellent post. I used to be checking constantly this blog and I am impressed! Extremely useful info specifically the ultimate part 🙂 I handle such information a lot. I was looking for this certain information for a very lengthy time. Thanks and best of luck.
This is the perfect site for anybody who really wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost tough to argue with you (not that I really will need to…HaHa). You definitely put a brand new spin on a subject that’s been written about for a long time. Excellent stuff, just excellent.
Hi, I do think this is a great website. I stumbledupon it 😉 I’m going to return once again since i have bookmarked it. Money and freedom is the greatest way to change, may you be rich and continue to guide others.
Thanks for putting this up. It’s well done.
You’ve clearly researched well.
You should be a part of a contest for one of the best blogs on the internet. I will recommend this site!
Thanks for publishing. It’s top quality.
hi!,I like your writing very so much! proportion we keep up a correspondence more approximately your article on AOL? I require a specialist on this area to resolve my problem. Maybe that is you! Having a look forward to look you.
I found new insight from this.
Hi there! This post couldn’t be written any better! Reading this post reminds me of my old room mate! He always kept talking about this. I will forward this article to him. Fairly certain he will have a good read. Many thanks for sharing!
Such a practical read.
This article is a breath of fresh air! The author’s unique perspective and perceptive analysis have made this a truly fascinating read. I’m appreciative for the effort she has put into producing such an informative and thought-provoking piece. Thank you, author, for providing your knowledge and igniting meaningful discussions through your outstanding writing!
The breadth in this article is remarkable.
You’ve clearly put in effort.
Woah! I’m really digging the template/theme of this blog. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s very difficult to get that “perfect balance” between user friendliness and appearance. I must say that you’ve done a fantastic job with this. Also, the blog loads very fast for me on Opera. Outstanding Blog!
I took away a great deal from this.
Hey there! I’ve been following your blog for a while now and finally got the courage to go ahead and give you a shout out from Humble Texas! Just wanted to tell you keep up the good work!
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I have joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your wonderful post. Also, I’ve shared your web site in my social networks!
It?s in point of fact a great and helpful piece of information. I am satisfied that you shared this useful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thank you again
Hey! I could have sworn I’ve been to this blog before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m definitely delighted I found it and I’ll be book-marking and checking back often!
I should say also believe that mesothelioma is a extraordinary form of most cancers that is usually found in those people previously subjected to asbestos. Cancerous cellular material form in the mesothelium, which is a safety lining that covers a lot of the body’s bodily organs. These cells usually form from the lining of the lungs, mid-section, or the sac that encircles one’s heart. Thanks for giving your ideas.
There is certainly a lot to find out about this topic. I like all the points you’ve made.
I appreciate this information. Thanks for breaking it down so clearly.
I think other website proprietors should take this site as an model, very clean and great user genial style and design, as well as the content. You are an expert in this topic!
Just desire to say your article is as surprising. The clarity in your post is just spectacular and i can assume you are an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission let me to grab your RSS feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please carry on the gratifying work.
Excellent crypto tool.
I appreciate this information. Bookmarking this for later.
Thanks for your post. One other thing is the fact that individual states in the United states of america have their own personal laws of which affect house owners, which makes it very, very hard for the the nation’s lawmakers to come up with a different set of rules concerning foreclosed on home owners. The problem is that each state has own guidelines which may interact in an adverse manner in terms of foreclosure insurance policies.
Also a thing to mention is that an online business administration study course is designed for learners to be able to effortlessly proceed to bachelor degree programs. The Ninety credit diploma meets the other bachelor college degree requirements so when you earn your associate of arts in BA online, you should have access to the newest technologies on this field. Several reasons why students want to be able to get their associate degree in business is because they can be interested in this area and want to obtain the general education necessary in advance of jumping into a bachelor diploma program. Thanks for the tips you actually provide within your blog.
Thought-provoking read. This cleared up a lot of confusion I had.
I’ve been using sativa tincture ordinary for during the course of a month for the time being, and I’m truly impressed at near the positive effects. They’ve helped me feel calmer, more balanced, and less anxious in every nook the day. My saw wood is deeper, I wake up refreshed, and even my focus has improved. The trait is excellent, and I cognizant the natural ingredients. I’ll obviously preserve buying and recommending them to everybody I identify!
Have you ever considered writing an e-book or guest authoring on other sites? I have a blog based upon on the same ideas you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my subscribers would appreciate your work. If you’re even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an e-mail.
Secure crypto exchange, no issues ever.
Great user interface, easy crypto trading.
It’s a shame you don’t have a donate button! I’d most certainly donate to this brilliant blog! I suppose for now i’ll settle for book-marking and adding your RSS feed to my Google account. I look forward to brand new updates and will share this site with my Facebook group. Chat soon!
Magnificent web site. A lot of useful info here. I?m sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thanks for your sweat!
Interesting perspective. Bookmarking this for later.
Best website I’ve seen in the USA.
Perfect platform for businesses.
You’re so interesting! I don’t suppose I’ve truly read a single thing like this before. So good to discover someone with original thoughts on this subject matter. Really.. many thanks for starting this up. This website is one thing that is needed on the web, someone with some originality.
Thanks for another excellent article. The place else may anybody get that kind of information in such an ideal way of writing? I’ve a presentation subsequent week, and I’m at the search for such info.
I’ve observed that in the world of today, video games will be the latest rage with kids of all ages. There are occassions when it may be unattainable to drag young kids away from the video games. If you want the best of both worlds, there are plenty of educational activities for kids. Thanks for your post.
Someone necessarily lend a hand to make severely articles I’d state. This is the first time I frequented your website page and up to now? I amazed with the research you made to make this particular submit incredible. Excellent process!
Hey very cool site!! Man .. Beautiful .. Superb .. I’ll bookmark your web site and take the feeds also?I am happy to seek out numerous useful information right here in the submit, we want develop more strategies in this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
Greetings, I do think your website could possibly be having web browser compatibility issues. When I look at your web site in Safari, it looks fine however when opening in IE, it has some overlapping issues. I simply wanted to provide you with a quick heads up! Apart from that, fantastic website.
Hmm it seems like your site ate my first comment (it was extremely long) so I guess I’ll just sum it up what I wrote and say, I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I too am an aspiring blog writer but I’m still new to everything. Do you have any suggestions for inexperienced blog writers? I’d certainly appreciate it.
Hmm is anyone else encountering problems with the pictures on this blog loading? I’m trying to determine if its a problem on my end or if it’s the blog. Any feed-back would be greatly appreciated.
I’ve been surfing online more than three hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It is pretty worth enough for me. In my view, if all webmasters and bloggers made good content as you did, the net will be much more useful than ever before.
Thank you for sharing superb informations. Your website is so cool. I’m impressed by the details that you have on this site. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for more articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found just the info I already searched everywhere and just could not come across. What an ideal web site.
It’s difficult to find educated people for this topic, however, you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Howdy! This article couldn’t be written any better! Going through this article reminds me of my previous roommate! He continually kept preaching about this. I most certainly will send this article to him. Pretty sure he’ll have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
Another thing I’ve noticed is the fact for many people, bad credit is the consequence of circumstances above their control. One example is they may have been saddled with illness and because of this they have substantial bills for collections. Maybe it’s due to a work loss or the inability to do the job. Sometimes breakup can really send the financial situation in the wrong direction. Thanks sharing your opinions on this website.
Does your site have a contact page? I’m having problems locating it but, I’d like to shoot you an email. I’ve got some ideas for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great site and I look forward to seeing it improve over time.
I just like the valuable info you supply to your articles. I will bookmark your weblog and test again here frequently. I’m moderately sure I will be told a lot of new stuff right right here! Good luck for the next!
I have really learned result-oriented things from the blog post. One more thing to I have seen is that in many instances, FSBO sellers will reject people. Remember, they will prefer to not ever use your products and services. But if anyone maintain a comfortable, professional partnership, offering guide and keeping contact for about four to five weeks, you will usually be capable to win interviews. From there, a house listing follows. Thanks
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this blog. It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s difficult to get that “perfect balance” between user friendliness and visual appeal. I must say you’ve done a very good job with this. Also, the blog loads extremely fast for me on Chrome. Exceptional Blog!
Hiya, I am really glad I’ve found this info. Today bloggers publish just about gossips and net and this is really irritating. A good website with interesting content, that’s what I need. Thanks for keeping this site, I will be visiting it. Do you do newsletters? Cant find it.
I’ve noticed that credit score improvement activity has to be conducted with techniques. If not, you will probably find yourself damaging your positioning. In order to reach your goals in fixing to your credit rating you have to ensure that from this time you pay your entire monthly dues promptly before their scheduled date. It is definitely significant since by not really accomplishing so, all other steps that you will choose to use to improve your credit standing will not be effective. Thanks for revealing your strategies.
At this time it appears like WordPress is the top blogging platform out there right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
There are definitely a lot of details like that to take into consideration. That is a nice level to convey up. I provide the thoughts above as basic inspiration but clearly there are questions like the one you bring up where a very powerful factor will be working in sincere good faith. I don?t know if finest practices have emerged round things like that, however I’m sure that your job is clearly recognized as a fair game. Both girls and boys feel the impact of just a second?s pleasure, for the rest of their lives.
My developer is trying to convince me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on numerous websites for about a year and am concerned about switching to another platform. I have heard great things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my wordpress posts into it? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Terrific work! This is the type of information that should be shared around the net. Shame on Google for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my website . Thanks =)
In these days of austerity in addition to relative anxiousness about running into debt, some people balk against the idea of making use of a credit card to make acquisition of merchandise as well as pay for a vacation, preferring, instead only to rely on a tried as well as trusted means of making settlement – cash. However, if you possess cash there to make the purchase completely, then, paradoxically, that is the best time to use the credit card for several reasons.
I just could not depart your website before suggesting that I really enjoyed the standard info a person provide for your visitors? Is going to be back often to check up on new posts
I have realized that of all forms of insurance, health insurance coverage is the most dubious because of the issue between the insurance policy company’s obligation to remain adrift and the user’s need to have insurance cover. Insurance companies’ profits on overall health plans have become low, thus some businesses struggle to make money. Thanks for the thoughts you talk about through this blog.
I have seen that wise real estate agents all over the place are Promoting. They are knowing that it’s more than merely placing a poster in the front area. It’s really concerning building relationships with these traders who at some time will become buyers. So, once you give your time and energy to helping these vendors go it alone — the “Law involving Reciprocity” kicks in. Thanks for your blog post.
Tracking trades sharpens skills
Some altcoins have surprising use cases.